A novel pathogenic missense variant in CNNM4 underlying Jalili syndrome: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 31347285
- PMCID: PMC6732295
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.902
A novel pathogenic missense variant in CNNM4 underlying Jalili syndrome: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
Background: Jalili syndrome (JS) is a rare cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) associated with amelogenesis imperfecta (AI). The first clinical presentation of JS patients was published in 1988 by Jalili and Smith. Pathogenic mutations in the Cyclin and CBS Domain Divalent Metal Cation Transport Mediator 4 (CNNM4) magnesium transporter protein have been reported as the leading cause of this anomaly.
Methods: In the present study, a clinical and genetic investigation was performed in a consanguineous family of Pakistani origin, showing characteristic features of JS. Sanger sequencing was successfully used to identify the causative variant in CNNM4. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to study the effect of amino acid change over CNNM4 protein.
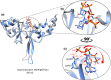
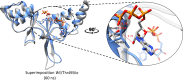
Results: Sequence analysis of CNNM4 revealed a novel missense variant (c.1220G>T, p.Arg407Leu) in exon-1 encoding cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) domain. To comprehend the mutational consequences in the structure, the mutant p.Arg407Leu was modeled together with a previously reported variant (c.1484C>T, p.Thr495Ile) in the same domain. Additionally, docking analysis deciphered the binding mode of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) cofactor. Furthermore, 60ns MD simulations were carried out on wild type (p.Arg407/p.Thr495) and mutants (p.Arg407Leu/p.Thr495Ile) to understand the structural and energetic changes in protein structure and its dynamic behavior. An evident conformational shift of ATP in the binding site was observed in simulated mutants disrupting the native ATP-binding mode.
Conclusion: The novel identified variant in CNNM4 is the first report from the Pakistani population. Overall, the study is valuable and may give a novel insight into metal transport in visual function and biomineralization.
Keywords: CNNM4; CBS domain; Jalili Syndrome; MD Simulations; missense variant.
© 2019 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflict of interest in the form of relationship, and finances which could have affected the current study.
Figures


References
-
- Abu‐Safieh, L. , Alrashed, M. , Anazi, S. , Alkuraya, H. , Khan, A. O. , Al‐Owain, M. , … Al‐Tarimi, S. (2012). Autozygome‐guided exome sequencing in retinal dystrophy patients reveals pathogenetic mutations and novel candidate disease genes. Genome Research, 23, 236–247. 10.1101/gr.144105.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abu‐Safieh, L. , Alrashed, M. , Anazi, S. , Alkuraya, H. , Khan, A. O. , Al‐Owain, M. , … Alkuraya, F. S. (2013). Autozygome‐guided exome sequencing in retinal dystrophy patients reveals pathogenetic mutations and novel candidate disease genes. Genome Research, 23(2), 236–247. 10.1101/gr.144105.112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

