Silencing of LncRNA-ANCR Promotes the Osteogenesis of Osteoblast Cells in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis via Targeting EZH2 and RUNX2
- PMID: 31347330
- PMCID: PMC6660440
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.8.751
Silencing of LncRNA-ANCR Promotes the Osteogenesis of Osteoblast Cells in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis via Targeting EZH2 and RUNX2
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the effects and mechanisms of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) anti-differentiation non-coding RNA (ANCR) on the osteogenesis of osteoblast cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMOP).
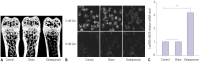
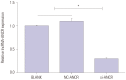
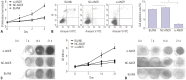
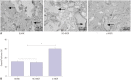
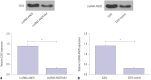
Materials and methods: Mice models of PMOP were established. ANCR expression and intracellular calcium ions were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and laser confocal microscopy, respectively. ANCR was silenced in osteoblast cells from PMOP mice by the transfection of siRNA-ANCR (si-ANCR). The proliferation and apoptosis of osteoblast cells was analyzed by MTT and flow cytometry, respectively. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and calcium nodules were examined by ALP and alizarin red staining assay, respectively. The expression of enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), runt related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), and OSTERIX was detected by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Furthermore, an osteogenesis model was constructed in mice, and osteoid formation was observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. The interaction between lncRNA-ANCR and EZH2 was further identified by RNA pull-down assay.
Results: ANCR expression and intracellular calcium ions were increased in PMOP mice. Si-ANCR significantly increased the proliferation, ALP activity, calcium deposition of osteoblast cells and decreased apoptosis. ANCR and EZH2 were down-regulated by si-ANCR, while RUNX2 and OSTERIX were upregulated. Si-ANCR also promoted osteoid formation in mice treated with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate. In addition, ANCR specifically bound to EZH2.
Conclusion: Silencing ANCR promotes the osteogenesis of PMOP osteoblast cells. The specific binding of ANCR with EZH2 suppressed RUNX2, thereby inhibiting osteogenesis.
Keywords: EZH2; Postmenopausal osteoporosis; RUNX2; lncRNA-ANCR; osteoblast; siRNA.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Downregulated LncRNA-ANCR promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting EZH2 and regulating Runx2 expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Mar 22;432(4):612-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.02.036. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23438432
-
Long noncoding RNA ANCR suppresses bone formation of periodontal ligament stem cells via sponging miRNA-758.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 5;503(2):815-821. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.081. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29913147
-
LncRNA-ANCR regulates the cell growth of osteosarcoma by interacting with EZH2 and affecting the expression of p21 and p27.J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 Jul 5;12(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0599-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28679390 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX2 regulation in osteoblast differentiation: A possible therapeutic function of the lncRNA and miRNA-mediated network.Differentiation. 2024 Nov-Dec;140:100803. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2024.100803. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Differentiation. 2024. PMID: 39089986 Review.
-
Regulation of Skeletal Development and Maintenance by Runx2 and Sp7.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 20;25(18):10102. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810102. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 silencing and microRNA-214 restoration elevate osteoprotegerin expression to ameliorate osteoporosis by limiting TXNIP.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Feb;25(4):2025-2039. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16096. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. Retraction in: J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Jan;27(2):309. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17601. PMID: 33393160 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Roles of lncRNA in the crosstalk between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in the bone microenvironment.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2025 Feb 25;26(2):107-123. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300607. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2025. PMID: 40015932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Icariin Promotes the Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Regulating Sclerostin and Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jan 22;2021:6666836. doi: 10.1155/2021/6666836. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33553429 Free PMC article.
-
Dancr-BRG1 regulates Nfatc1 transcription and Pgc1β-dependent metabolic shifts in osteoclastogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 30;121(5):e2313656121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313656121. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38252822 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of lncRNAs in osteoporosis.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 May;39(3):341-352. doi: 10.1007/s00774-021-01205-6. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33566207 Review.
References
-
- Black DM, Rosen CJ. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2096–2097. - PubMed
-
- Wade SW, Strader C, Fitzpatrick LA, Anthony MS, O'Malley CD. Estimating prevalence of osteoporosis: examples from industrialized countries. Arch Osteoporos. 2014;9:182. - PubMed
-
- Gennari L, Rotatori S, Bianciardi S, Nuti R, Merlotti D. Treatment needs and current options for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17:1141–1152. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

