Voice break in boys-temporal relations with other pubertal milestones and likely causal effects of BMI
- PMID: 31348498
- PMCID: PMC6688887
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dez118
Voice break in boys-temporal relations with other pubertal milestones and likely causal effects of BMI
Abstract
Study question: How is timing of voice break related to other male pubertal milestones as well as to BMI?
Summary answer: We provide a comprehensive temporal analysis of male pubertal milestones, including reproductive hormone dynamics, confirm voice break as a late milestone of male puberty and report a likely causal relationship between higher BMI and earlier age at voice break in men.
What is known already: Voice break represents a late pubertal milestone and recalled age at voice break is frequently used in epidemiological studies as a measure of puberty. In contrast, clinical studies use mainly testicular enlargement and/or genital tanner stage as the marker of pubertal onset. However, neither correlation of pubertal milestones nor reproductive hormone dynamics have been assessed in detail previously. Further, although BMI and puberty timing are known to be closely linked, cause and effect between these traits are not known.
Study design, size, duration: The study included a population-based mixed cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort (2006-2014, COPENHAGEN Puberty Study) of 730 healthy Danish boys. Data for 55 871 male research participants from the 23andMe study were obtained, including genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism data and age at voice break.
Participants/materials, setting, methods: We performed a detailed evaluation of pubertal milestones and reproductive hormone levels (study population 1). A Mendelian randomization (MR) approach was used to determine the likely causal link between BMI and timing of voice break (study population 2).
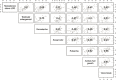
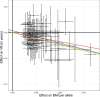
Main results and the role of chance: Voice break occurred at mean age 13.6 (95% CI: 13.5-13.8) years. At voice break, mean (95% CI) testosterone levels, LH levels and bi-testicular volume were 10.9 (10.0-11.7) nmol/L, 2.4 (2.2-2.5) IU/L and 24 (23-25) mL, respectively. Voice break correlated moderately strongly with timing of male pubertal milestones, including testicular enlargement, gonadarche, pubarche, sweat odor, axillary hair growth and testosterone above limit of detection (r2 range: 0.43-0.61). Timing of all milestones was negatively associated with age-specific BMI (all P ≤ 0.001). MR analyses inferred likely causal effects of higher BMI on earlier voice break in males (-0.35 years/approximate SD, P < 0.001).
Limitations, reasons for caution: Participation rate of the population-based cohort was 25%. Further, boys that were followed longitudinally were examined approximately every 6 months limiting the time resolution of pubertal milestones. Using adult BMI as exposure instead of prepubertal BMI in the MR analysis and the known inaccuracies of the testosterone immunoassay at low testosterone levels may be further limitations.
Wider implications of the findings: We provide valuable normative data on the temporal relation of male pubertal milestones. Further, the likely causal relationship between BMI and puberty timing highlights the importance of preventing obesity in childhood.
Study funding/competing interest(s): This work was supported by Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation (09-067 180); Danish Ministry of the Environment, CeHoS (MST-621-00 065); Capital Region of Denmark (R129-A3966); Ministry of Higher Education and Science (DFF-1331-00 113); Innovation Fund Denmark (InnovationsFonden, 14-2013-4); The International Center for Research and Research Training in Endocrine Disrupting Effects of Male Reproduction and Child Health. B.H., F.R.D., J.R.B.P. and K.K.O. are supported by the Medical Research Council (MC_UU_12015/2). The 23andMe study is supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute of the National Institutes of Health (R44HG006981). Members of the 23andMe Research Team are employees of 23andMe, Inc. and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe.
Trial registration number: NCT01411527.
Keywords: BMI; Mendelian randomization; causal; male; puberty; voice break.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Self-reported onset of puberty and subsequent semen quality and reproductive hormones in healthy young men.Hum Reprod. 2016 Aug;31(8):1886-94. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew122. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27270973
-
Parental time to pregnancy, medically assisted reproduction and pubertal development in boys and girls.Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):724-732. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez008. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30753468 Free PMC article.
-
Puberty timing and adiposity change across childhood and adolescence: disentangling cause and consequence.Hum Reprod. 2020 Dec 1;35(12):2784-2792. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa213. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 33242326 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal and postnatal exposures to endocrine disrupting chemicals and timing of pubertal onset in girls and boys: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod Update. 2022 Aug 25;28(5):687-716. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmac013. Hum Reprod Update. 2022. PMID: 35466359 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology and timing of male puberty.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012 Jun;19(3):197-203. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283535614. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012. PMID: 22499221 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation and comparison of nine growth and development-based measures of pubertal timing.Commun Med (Lond). 2024 Aug 7;4(1):159. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00580-1. Commun Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39112679 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-Puberty, Physiological and Disordered: Consequences, and Potential for Therapeutic Replacement.Endocr Rev. 2024 Jul 12;45(4):460-492. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnae003. Endocr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38436980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal programming of developmental trajectories for obesity risk and early pubertal timing.Dev Psychol. 2022 Oct;58(10):1817-1831. doi: 10.1037/dev0001405. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Dev Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35727305 Free PMC article.
-
Association between pubertal timing and bone and body composition in young adult men.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 19;15(1):9506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93895-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40108242 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Puberty Timing and Body Mass Index in a Longitudinal Setting: The Contribution of Genetic Factors.Behav Genet. 2022 May;52(3):186-194. doi: 10.1007/s10519-022-10100-3. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Behav Genet. 2022. PMID: 35381915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed ML, Ong KK, Dunger DB. Childhood obesity and the timing of puberty. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2009;20:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Aksglaede L, Sorensen K, Petersen JH, Skakkebaek NE, Juul A. Recent decline in age at breast development: the Copenhagen Puberty Study. Pediatrics 2009b;123:e932–e939. - PubMed
-
- Andersen E. Skeletal maturation of Danish school children in relation to height, sexual development, and social conditions. Acta Paediatr Scand 1968; Suppl 185:111+. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

