The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induces DNA damage in Ph+ leukemia and sensitizes for ABL kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 31349760
- PMCID: PMC6738521
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1646068
The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induces DNA damage in Ph+ leukemia and sensitizes for ABL kinase inhibitors
Abstract
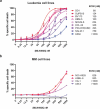
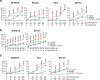
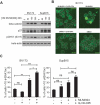
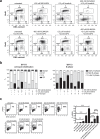
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene is the driver oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia-chromosome positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting the ABL kinase (such as imatinib) has dramatically improved survival of CML and Ph+ ALL patients. However, primary and acquired resistance to TKIs remains a clinical challenge. Ph+ leukemia patients who achieve a complete cytogenetic (CCR) or deep molecular response (MR) (≥4.5log reduction in BCR-ABL1 transcripts) represent long-term survivors. Thus, the fast and early eradication of leukemic cells predicts MR and is the prime clinical goal for these patients. We show here that the first-in-class inhibitor of the Nedd8-activating enzyme (NAE1) MLN4924 effectively induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in Ph+ leukemia cells, and sensitized leukemic cells for ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) and hydroxyurea (HU). We demonstrate that MLN4924 induced DNA damage in Ph+ leukemia cells by provoking the activation of an intra S-phase checkpoint, which was enhanced by imatinib co-treatment. The combination of MLN4924 and imatinib furthermore triggered a dramatic shift in the expression of MCL1 and NOXA. Our data offers a clear rationale to explore the clinical activity of MLN4924 (alone and in combination with ABL TKI) in Ph+ leukemia patients.
Keywords: DNA damage; Neddylation; Ph+ leukemia.
Figures

References
-
- Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GAN, et al. Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the medical research council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern cooperative oncology group (ECOG) 2993 trial. Blood. 2007;109:3189–3197. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Neriah Y, Daley GQ, Mes-Masson AM, et al. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986;233:212–214. - PubMed
-
- Van Etten RA, Jackson P, Baltimore D.. The mouse type IV c-abl gene product is a nuclear protein, and activation of transforming ability is associated with cytoplasmic localization. Cell. 1989;58:669–678. - PubMed
-
- Shuai K, Halpern J, Ten Hoeve J, et al. Constitutive activation of STAT5 by the BCR-ABL oncogene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene. 1996;13:247–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
