Protein Amounts of the MYC Transcription Factor Determine Germinal Center B Cell Division Capacity
- PMID: 31350178
- PMCID: PMC6703930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.013
Protein Amounts of the MYC Transcription Factor Determine Germinal Center B Cell Division Capacity
Abstract
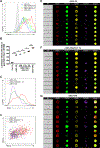
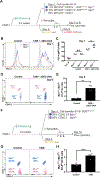
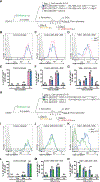
High-affinity B cell selection in the germinal center (GC) is governed by signals delivered by follicular helper T (Tfh) cells to B cells. Selected B cells undergo clonal expansion and affinity maturation in the GC dark zone in direct proportion to the amount of antigen they capture and present to Tfh cells in the light zone. Here, we examined the mechanisms whereby Tfh cells program the number of GC B cell divisions. Gene expression analysis revealed that Tfh cells induce Myc expression in light-zone B cells in direct proportion to antigen capture. Conditional Myc haplo-insufficiency or overexpression combined with cell division tracking showed that MYC expression produces a metabolic reservoir in selected light-zone B cells that is proportional to the number of cell divisions in the dark zone. Thus, MYC constitutes the GC B cell division timer that when deregulated leads to emergence of B cell lymphoma.
Keywords: B cell; MYC; antibody; cell cycle; cell size; germinal center.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



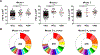
References
-
- Allen CD, Ansel KM, Low C, Lesley R, Tamamura H, Fujii N, and Cyster JG (2004). Germinal center dark and light zone organization is mediated by CXCR4 and CXCR5. Nat Immunol 5, 943–952. - PubMed
-
- Allen CD, Okada T, Tang HL, and Cyster JG (2007). Imaging of germinal center selection events during affinity maturation. Science 315, 528–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

