Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens
- PMID: 31350381
- PMCID: PMC6744578
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20180053
Role of prolyl hydroxylation in the molecular interactions of collagens
Abstract
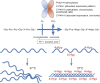
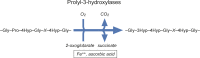
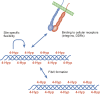
Co- and post-translational hydroxylation of proline residues is critical for the stability of the triple helical collagen structure. In this review, we summarise the biology of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases and collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylases, the enzymes responsible for proline hydroxylation. Furthermore, we describe the potential roles of hydroxyproline residues in the complex interplay between collagens and other proteins, especially integrin and discoidin domain receptor type cell adhesion receptors. Qualitative and quantitative regulation of collagen hydroxylation may have remarkable effects on the properties of the extracellular matrix and consequently on the cell behaviour.
Keywords: collagen; extracellular matrix; integrins; molecular interactions; prolyl hydroxylase.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.M. owns equity in FibroGen Inc., which develops HIF-P4H inhibitors as potential therapeutics. This company supports HIF-related research in the J.M. group.
Figures
References
-
- Kivirikko K.I., Myllylä R. and Pihlajaniemi T. (1992) Prolyl hydroxylase, protein disulfide isomerase, and other structurally related proteins. In Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins(Harding J.J. and Crabbe M.J.C., eds), pp. 1–51, CRC Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

