Revealing dynamic regulations and the related key proteins of myeloma-initiating cells by integrating experimental data into a systems biological model
- PMID: 31350562
- PMCID: PMC8485849
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz542
Revealing dynamic regulations and the related key proteins of myeloma-initiating cells by integrating experimental data into a systems biological model
Abstract
Motivation: The growth and survival of myeloma cells are greatly affected by their surrounding microenvironment. To understand the molecular mechanism and the impact of stiffness on the fate of myeloma-initiating cells (MICs), we develop a systems biological model to reveal the dynamic regulations by integrating reverse-phase protein array data and the stiffness-associated pathway.
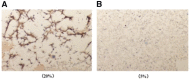
Results: We not only develop a stiffness-associated signaling pathway to describe the dynamic regulations of the MICs, but also clearly identify three critical proteins governing the MIC proliferation and death, including FAK, mTORC1 and NFκB, which are validated to be related with multiple myeloma by our immunohistochemistry experiment, computation and manually reviewed evidences. Moreover, we demonstrate that the systematic model performs better than widely used parameter estimation algorithms for the complicated signaling pathway.
Availability and implementation: We can not only use the systems biological model to infer the stiffness-associated genetic signaling pathway and locate the critical proteins, but also investigate the important pathways, proteins or genes for other type of the cancer. Thus, it holds universal scientific significance.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





References
-
- Abe M. (2011) Targeting the interplay between myeloma cells and the bone marrow microenvironment in myeloma. Int. J. Hematol., 94, 334–343. - PubMed
-
- Anderson K.C. (2007) Targeted therapy of multiple myeloma based upon tumor-microenvironmental interactions. Exp. Hematol., 35 (4 Suppl. 1), 155–162. - PubMed
-
- Apostolos Z. et al. (2014) Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA). Oncoscience, 1, 117.
-
- Chaouiya C. (2007) Petri net modelling of biological networks. Brief. Bioinform., 8, 210–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R50 CA221675/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2017YFA0505500/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- XDB13040700/Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 61372138/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018ZX10201002/the National Science and Technology Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

