High-Density Lipoprotein in Lupus: Disease Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Strategy
- PMID: 31350818
- PMCID: PMC6935404
- DOI: 10.1002/art.41059
High-Density Lipoprotein in Lupus: Disease Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Strategy
Abstract
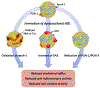
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients exhibit accelerated development of atherosclerosis and increased incidents of cardiovascular disease (CVD) that cannot be explained by traditional risk factors alone. Accumulating evidence suggests that reduced levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDLs), along with altered HDL composition and function, may contribute to the accelerated atherosclerosis in SLE patients. Normally, HDLs play various atheroprotective roles through facilitating cholesterol efflux, inhibiting vascular inflammation, and scavenging oxidative species. However, systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and autoimmunity in SLE patients induce changes in HDL size distribution and proteomic and lipidomic signatures. These compositional changes in HDLs result in the formation of proinflammatory, dysfunctional HDL. These lupus-altered HDLs have impaired antiatherogenic function with reduced cholesterol efflux capacities, impaired antioxidation abilities, and diminished antiinflammatory properties. In fact, dysfunctional HDL may promote atherogenesis by inducing inflammation. Thus, dysfunctional HDLs could be an important biomarker of accelerated atherosclerosis in lupus. Additionally, HDL-targeted therapies, especially infusion of reconstituted HDLs, may serve as a potential therapeutic intervention for SLE patients with CVD.
© 2019, American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

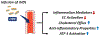
Comment in
-
Anti-Apolipoprotein A-I in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Comment on the Article by Kim et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jul;72(7):1233-1234. doi: 10.1002/art.41235. Epub 2020 May 31. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32103622 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jul;72(7):1234-1236. doi: 10.1002/art.41237. Epub 2020 May 28. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32103638 No abstract available.
References
-
- Urowitz MB, Gladman DD, Tom BDM, Ibañez D & Farewell VT Changing patterns in mortality and disease outcomes for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol 35, 2152–8 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Bernatsky S et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2550–2557 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Elliott JR & Manzi S Atherosclerosis risk factors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep 11, 241–247 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lerang K, Gilboe I-M, Steinar Thelle D & Gran JT Mortality and years of potential life loss in systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based cohort study. Lupus 23, 1546–1552 (2014). - PubMed

