The first-generation phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and their pharmacokinetic issue
- PMID: 31350821
- PMCID: PMC6790582
- DOI: 10.1111/andr.12683
The first-generation phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and their pharmacokinetic issue
Abstract
Background: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a relatively frequent disease that negatively impacts the overall quality of life, well-being, and relationships. Although the use of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE5is) has revolutionized the treatment of ED, a high percentage of ED patients discontinue PDE5i treatment.
Objectives: (i) To analyze the reasons for patient dissatisfaction leading to PDE5i discontinuation; (ii) analyze the pharmacokinetics of new formulations focusing on the time needed to reach an effective plasma concentration of PDE5is (Tonset ) following drug intake; and (iii) summarize the physicochemical properties of sildenafil to understand which excipients may increase the absorption rate.
Material and methods: An online PubMed literature search was conducted to identify English language publications from inception to January 2019.
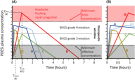
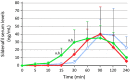
Results: The main reasons for patient dissatisfaction when using PDE5is on demand are the relatively long Tonset after taking vardenafil and sildenafil, including formulations such as film-coated tablets, fine granules, orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), and oral thin films (ODFs). The relatively long Tonset , further worsened when accompanied by eating, highlights the following: (i) the need for planning intercourse, determining partner-related issues; (ii) issues when having sex before the maximum effect of the drug; and (iii) lower drug-related placebo effects. Some data suggest that sildenafil is a 'difficult' molecule, but Tonset can be improved following absorption by buccal mucosa using appropriate excipients.
Conclusions: We conclude that several ODT and ODF formulations can improve the 'discretion' issue because they are taken without water, but they have similar pharmacokinetics to corresponding film-coated tablet formulations. One ODF formulation of sildenafil was characterized by a shorter Tonset and could potentially increase patient satisfaction following treatment. However, more clinical studies are needed to confirm the findings. Surfactants and ascorbic acid appear to be crucial excipients for achieving a high absorption rate, but more studies are needed.
Keywords: ODF formulation; OTF formulation; PDE5 inhibitors; erectile dysfunction; excipients; pharmacokinetic.
© 2019 The Authors. Andrology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of American Society of Andrology and European Academy of Andrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Manuscript writing and editing were supported by SOFAR. However, SOFAR did not participate in study conception and manuscript writing. Giuseppe Nocentini is a consultant of Pieris Pharmaceuticals and Amgen. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aguirre LG, Olmedo IR, Nolasco AM, Romo YI, Reyes LM, Hernández DAA & Vargas ALR. (2019) Comparative bioavailability of sildenafil 50‐mg film‐coated tablets and 50‐mg orally disintegrating films in healthy Mexican subjects: results from a randomized, open‐label, crossover study. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 8, 404–410. - PubMed
-
- Althof SE, O'leary MP, Cappelleri JC, Hvidsten K, Stecher VJ, Glina S, King R, Siegel RL & International SEAR Study Group . (2006) Sildenafil citrate improves self‐esteem, confidence, and relationships in men with erectile dysfunction: results from an international, multi‐center, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. J Sex Med 3, 521–529. - PubMed
-
- Benedetti F. (2014) Placebo effects: from the neurobiological paradigm to translational implications. Neuron 84, 623–637. - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs R, Fourcade R, Kiemeney L, Lee C & UrEpik Study Group . (2003) The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int 92, 719–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

