DeepGOPlus: improved protein function prediction from sequence
- PMID: 31350877
- PMCID: PMC9883727
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz595
DeepGOPlus: improved protein function prediction from sequence
Erratum in
-
DeepGOPlus: improved protein function prediction from sequence.Bioinformatics. 2021 May 23;37(8):1187. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa763. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34009304 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Motivation: Protein function prediction is one of the major tasks of bioinformatics that can help in wide range of biological problems such as understanding disease mechanisms or finding drug targets. Many methods are available for predicting protein functions from sequence based features, protein-protein interaction networks, protein structure or literature. However, other than sequence, most of the features are difficult to obtain or not available for many proteins thereby limiting their scope. Furthermore, the performance of sequence-based function prediction methods is often lower than methods that incorporate multiple features and predicting protein functions may require a lot of time.
Results: We developed a novel method for predicting protein functions from sequence alone which combines deep convolutional neural network (CNN) model with sequence similarity based predictions. Our CNN model scans the sequence for motifs which are predictive for protein functions and combines this with functions of similar proteins (if available). We evaluate the performance of DeepGOPlus using the CAFA3 evaluation measures and achieve an Fmax of 0.390, 0.557 and 0.614 for BPO, MFO and CCO evaluations, respectively. These results would have made DeepGOPlus one of the three best predictors in CCO and the second best performing method in the BPO and MFO evaluations. We also compare DeepGOPlus with state-of-the-art methods such as DeepText2GO and GOLabeler on another dataset. DeepGOPlus can annotate around 40 protein sequences per second on common hardware, thereby making fast and accurate function predictions available for a wide range of proteins.
Availability and implementation: http://deepgoplus.bio2vec.net/ .
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
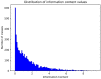
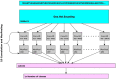

References
-
- Abadi M. et al. (2016) Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, OSDI’16, pp. 265–283. USENIX Association, Berkeley, CA, USA.
-
- Buchfink B. et al. (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using diamond. Nat. Methods, 12, 59.. - PubMed
-
- Davis J., Goadrich M. (2006) The relationship between precision–recall and roc curves. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML ’06, pp. 233–240. ACM, New York, NY, USA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

