Combined genetic disruption of K-Cl cotransporters and Gardos channel KCNN4 rescues erythrocyte dehydration in the SAD mouse model of sickle cell disease
- PMID: 31352162
- PMCID: PMC6744291
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102346
Combined genetic disruption of K-Cl cotransporters and Gardos channel KCNN4 rescues erythrocyte dehydration in the SAD mouse model of sickle cell disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Combined genetic disruption of K-Cl cotransporters and Gardos channel KCNN4 rescues erythrocyte dehydration in the SAD mouse model of sickle cell disease" [Blood Cells Mol. Dis. (2019) start page-end page not yet assigned] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102346.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020 Mar;81:102390. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102390. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31931456 No abstract available.
Abstract
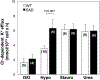
Excessive red cell dehydration contributes to the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease (SCD). The densest fraction of sickle red cells (with the highest corpuscular hemoglobin concentration) undergoes the most rapid polymerization of deoxy-hemoglobin S, leading to accelerated cell sickling and increased susceptibility to endothelial activation, red cell adhesion, and vaso-occlusion. Increasing red cell volume in order to decrease red cell density can thus serve as an adjunct therapeutic goal in SCD. Regulation of circulating mouse red cell volume and density is mediated largely by the Gardos channel, KCNN4, and the K-Cl cotransporters, KCC3 and KCC1. Whereas inhibition of the Gardos channel in subjects with sickle cell disease increased red cell volume, decreased red cell density, and improved other hematological indices in subjects with SCD, specific KCC inhibitors have not been available for testing. We therefore investigated the effect of genetic inactivation of KCC3 and KCC1 in the SAD mouse model of sickle red cell dehydration, finding decreased red cell density and improved hematological indices. We describe here generation of mice genetically deficient in the three major red cell volume regulatory gene products, KCNN4, KCC3, and KCC1 in C57BL6 non-sickle and SAD sickle backgrounds. We show that combined loss-of-function of all three gene products in SAD mice leads to incrementally increased MCV, decreased CHCM and % hyperchromic cells, decreased red cell density (phthalate method), increased resistance to hypo-osmotic lysis, and increased cell K content. The data show that combined genetic deletion of the Gardos channel and K-Cl cotransporters in a mouse SCD model decreases red cell density and improves several hematological parameters, supporting the strategy of combined pharmacological inhibition of these ion transport pathways in the adjunct treatment of human SCD.
Keywords: Osmotic fragility; Potassium channel; Potassium transporter; Red blood cell; Splenomegaly.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest:
The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
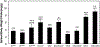


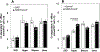

References
-
- Ataga KI, Reid M, Ballas SK, Yasin Z, Bigelow C, James LS, Smith WR, Galacteros F, Kutlar A, Hull JH, Stocker JW, and Investigators ICAS. Improvements in haemolysis and indicators of erythrocyte survival do not correlate with acute vaso-occlusive crises in patients with sickle cell disease: a phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the Gardos channel blocker senicapoc (ICA-17043). British journal of haematology 153: 92–104, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Ataga KI, Smith WR, De Castro LM, Swerdlow P, Saunthararajah Y, Castro O, Vichinsky E, Kutlar A, Orringer EP, Rigdon GC, Stocker JW, and Investigators ICA. Efficacy and safety of the Gardos channel blocker, senicapoc (ICA-17043), in patients with sickle cell anemia. Blood 111: 3991–3997, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Begenisich T, Nakamoto T, Ovitt CE, Nehrke K, Brugnara C, Alper SL, and Melvin JE. Physiological roles of the intermediate conductance, Ca2+-activated potassium channel Kcnn4. The Journal of biological chemistry 279: 47681–47687, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Brendel C, Guda S, Renella R, Bauer DE, Canver MC, Kim YJ, Heeney MM, Klatt D, Fogel J, Milsom MD, Orkin SH, Gregory RI, and Williams DA. Lineage-specific BCL11A knockdown circumvents toxicities and reverses sickle phenotype. The Journal of clinical investigation 126: 3868–3878, 2016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brugnara C, De Franceschi L, and Alper SL. Ca(2+)-activated K+ transport in erythrocytes. Comparison of binding and transport inhibition by scorpion toxins. The Journal of biological chemistry 268: 8760–8768, 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

