MALVA: Genotyping by Mapping-free ALlele Detection of Known VAriants
- PMID: 31352182
- PMCID: PMC6664100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.07.011
MALVA: Genotyping by Mapping-free ALlele Detection of Known VAriants
Abstract
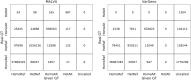
The amount of genetic variation discovered in human populations is growing rapidly leading to challenging computational tasks, such as variant calling. Standard methods for addressing this problem include read mapping, a computationally expensive procedure; thus, mapping-free tools have been proposed in recent years. These tools focus on isolated, biallelic SNPs, providing limited support for multi-allelic SNPs and short insertions and deletions of nucleotides (indels). Here we introduce MALVA, a mapping-free method to genotype an individual from a sample of reads. MALVA is the first mapping-free tool able to genotype multi-allelic SNPs and indels, even in high-density genomic regions, and to effectively handle a huge number of variants. MALVA requires one order of magnitude less time to genotype a donor than alignment-based pipelines, providing similar accuracy. Remarkably, on indels, MALVA provides even better results than the most widely adopted variant discovery tools.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Biological Sciences; Genetics; Genomics.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Eggertsson H.P., Jonsson H., Kristmundsdottir S., Hjartarson E., Kehr B., Masson G., Zink F., Hjorleifsson K.E., Jonasdottir A., Jonasdottir A. Graphtyper enables population-scale genotyping using pangenome graphs. Nat. Genet. 2017;49:1654–1660. - PubMed

