miR-451 Silencing Inhibited Doxorubicin Exposure-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice
- PMID: 31355248
- PMCID: PMC6637715
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1528278
miR-451 Silencing Inhibited Doxorubicin Exposure-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice
Abstract
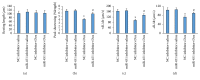
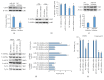
Oxidative stress and cardiomyocytes apoptosis were closely involved in the pathological process of doxorubicin- (Dox-) induced cardiac injury. MicroRNA-451 (miR-451) was mainly expressed in cardiomyocytes. However, the role of miR-451 in Dox-induced cardiac injury remained unclear. Our study aimed to investigate the effect of miR-451 on Dox-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. We established a Dox-induced cardiotoxicity model in the mice and manipulated miR-451 expression in the heart using a miR-451 inhibitor, which was injected every other day beginning at one day before Dox injection. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in the hearts were evaluated. miR-451 levels were significantly increased in Dox-treated mice or cardiomyocytes. miR-451 inhibition attenuated Dox-induced whole-body wasting and heart atrophy, reduced cardiac injury, restored cardiac function, and improved cardiomyocyte contractile function. Moreover, miR-451 inhibition reduced oxidative stress and cardiomyocytes apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. miR-451 inhibition increased the expression of calcium binding protein 39 (Cab39) and activated adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway. A specific inhibitor of AMPK abolished the protection provided by miR-451 inhibition against cell injury in vitro. In conclusion, miR-451 inhibition protected against Dox-induced cardiotoxicity via activation of AMPK signaling pathway.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

