First Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty: Investigation in Swine of a Prototype Partial Knee Endoprosthesis
- PMID: 31355275
- PMCID: PMC6634287
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6952649
First Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty: Investigation in Swine of a Prototype Partial Knee Endoprosthesis
Abstract
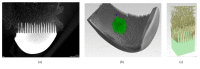
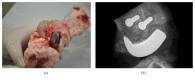
Resurfacing hip and knee endoprostheses are generally embedded in shallow, prepared areas in the bone and secured with cement. Massive cement penetration into periarticular bone, although it provides sufficient primary fixation, leads to the progressive weakening of peri-implant bone and results in failures. The aim of this paper was to investigate in an animal model the first biomimetic fixation of components of resurfacing arthroplasty endoprostheses by means of the innovative multispiked connecting scaffold (MSC-Scaffold). The partial resurfacing knee arthroplasty (RKA) endoprosthesis working prototype with the MSC-Scaffold was designed for biomimetic fixation investigations using reverse engineering methods and manufactured by selective laser melting. After Ca-P surface modification of bone contacting surfaces of the MSC-Scaffold, the working prototypes were implanted in 10 swines. Radiological, histopathological, and micro-CT examinations were performed on retrieved bone-implant specimens. Clinical examination confirmed very good stability (4 in 5-point Likert scale) of the operated knee joints. Radiological examinations showed good implant fixation (radiolucency less than 2 mm) without any signs of migration. Spaces between the MSC-Scaffold spikes were penetrated by bone tissue. The histological sections showed newly formed trabecular bone tissue between the spikes, and the trabeculae of periscaffold bone were seen in contact with the spikes. The micro-CT results showed the highest percentage of bone tissue ingrowths into the MSC-Scaffold at a distance of 2.5÷3.0 mm from the spikes bases. The first biomimetic fixation for resurfacing arthroplasty was successfully verified in 10 swines investigations using RKA endoprosthesis working prototypes. The performed research shows that the MSC-Scaffold allows for cementless and biomimetic fixation of resurfacing endoprosthesis components in periarticular cancellous bone.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;9(2):99. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9020099. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Multispiked Connecting Ti-Alloy Scaffold Prototype for Entirely-Cementless Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses-Exemplary Results of Implantation of the Ca-P Surface-Modified Scaffold Prototypes in Animal Model and Osteoblast Culture Evaluation.Materials (Basel). 2016 Jun 29;9(7):532. doi: 10.3390/ma9070532. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28773652 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary results of implantation in animal model and osteoblast culture evaluation of prototypes of biomimetic multispiked connecting scaffold for noncemented stemless resurfacing hip arthroplasty endoprostheses.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:689089. doi: 10.1155/2013/689089. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23984397 Free PMC article.
-
Structural-Geometric Functionalization of the Additively Manufactured Prototype of Biomimetic Multispiked Connecting Ti-Alloy Scaffold for Entirely Noncemented Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2017;2017:5638680. doi: 10.1155/2017/5638680. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2017. PMID: 28785159 Free PMC article.
-
[Bone defect management in revision knee arthroplasty].Orthopade. 2021 Dec;50(12):1004-1010. doi: 10.1007/s00132-021-04181-x. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Orthopade. 2021. PMID: 34654936 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Towards the First Generation of Biomimetic Fixation for Resurfacing Arthroplasty Endoprostheses.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;9(2):99. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9020099. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proposal for a Novel Abrasive Machining Method for Preparing the Surface of Periarticular Tissue during Orthopedic Surgery on Hip Joints.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Sep 8;12(3):50. doi: 10.3390/jfb12030050. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34564199 Free PMC article.
-
Subchondral Bone Relative Area and Density in Human Osteoarthritic Femoral Heads Assessed with Micro-CT before and after Mechanical Embedding of the Innovative Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold for Resurfacing THA Endoprostheses: A Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 30;10(13):2937. doi: 10.3390/jcm10132937. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34208953 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Density Micro-CT Assessment during Embedding of the Innovative Multi-Spiked Connecting Scaffold in Periarticular Bone to Elaborate a Validated Numerical Model for Designing Biomimetic Fixation of Resurfacing Endoprostheses.Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 12;14(6):1384. doi: 10.3390/ma14061384. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809176 Free PMC article.
-
Long Bone Defect Filling with Bioactive Degradable 3D-Implant: Experimental Study.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;8(2):138. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020138. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37092390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bose V. C., Baruah B. D. Resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip for avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a minimum follow-up of four years. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (British Volume) 2010;92(7):922–928. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

