Evaluation of Chondroprotective Activity of Channa striatus in Rabbit Osteoarthritis Model
- PMID: 31355276
- PMCID: PMC6636483
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6979585
Evaluation of Chondroprotective Activity of Channa striatus in Rabbit Osteoarthritis Model
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of the study is to evaluate the chondroprotective activity of Channa striatus (Channa) and glucosamine sulphate (glucosamine) on histomorphometric examinations, serum biomarker, and inflammatory mediators in experimental osteoarthritis (OA) rabbit model.
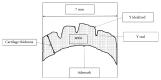
Design: Anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) was performed to induce OA in thirty-three male New Zealand white rabbits and were randomly divided into three groups: Channa, glucosamine, and control group. The control group received drinking water and the Channa and glucosamine groups were orally administered with 51.4 mg/kg of Channa extract and 77.5 mg/kg of glucosamine sulphate in drinking water, respectively, for eight weeks and then sacrificed. The articular cartilage was evaluated macroscopically and histologically using semiquantitative and quantitative methods. Serum cartilage oligomeric matric protein (COMP), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) enzyme, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) were also determined.
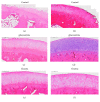
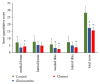
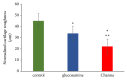
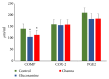
Results: Macroscopic analysis revealed that Channa group have a significantly lower severity grade of total macroscopic score compared to the control (p < 0.001) and glucosamine (p < 0.05) groups. Semiquantitative histology scoring showed that both Channa and glucosamine groups had lower severity grading of total histology score compared to the control group (p < 0.001). In comparison with the control, Channa group had lower histopathological changes in three compartments of the joint compared to glucosamine group which had lower histological scoring in two compartments only. The cartilage thickness, area, and roughness of both Channa (p < 0.05) and glucosamine (p < 0.05) groups were superior compared to the control group. However, the Channa group demonstrated significantly less cartilage roughness compared to the glucosamine group (p < 0.05). Serum COMP levels were lower in both Channa (p < 0.05) and glucosamine (p < 0.05) groups compared to the control group.
Conclusion: Both oral administration of Channa extract and glucosamine exhibited chondroprotective action on an ACLT OA-induced rabbit model. However, Channa was superior to glucosamine in maintaining the structure of the cartilage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Channa striatus in inflammatory conditions: A systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1076143. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1076143. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36545318 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the chondroprotective effects of glucosamine and fish collagen peptide on a rabbit ACLT model using serum biomarkers.J Vet Med Sci. 2013 May 2;75(4):421-9. doi: 10.1292/jvms.12-0240. Epub 2012 Nov 15. J Vet Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23154419
-
Inhibition of cartilage degradation and suppression of PGE2 and MMPs expression by pomegranate fruit extract in a model of posttraumatic osteoarthritis.Nutrition. 2017 Jan;33:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.08.004. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nutrition. 2017. PMID: 27908544 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oral glucosamine on cartilage degradation in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Apr;52(4):1118-28. doi: 10.1002/art.20951. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 15818693
-
The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rabbit.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010 Oct;18 Suppl 3:S53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.05.029. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010. PMID: 20864023
Cited by
-
Antibacterial and cytotoxic activity assessment of Channa striatus (Haruan) extract.Vet World. 2020 Mar;13(3):508-514. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.508-514. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Vet World. 2020. PMID: 32367957 Free PMC article.
-
Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate: Is There Any Scientific Evidence for Their Effectiveness as Disease-Modifying Drugs in Knee Osteoarthritis Preclinical Studies?-A Systematic Review from 2000 to 2021.Animals (Basel). 2021 May 29;11(6):1608. doi: 10.3390/ani11061608. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Channa striatus in inflammatory conditions: A systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1076143. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1076143. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36545318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausiello J. C., Stafford R. S. Trends in medication use for osteoarthritis treatment. The Journal of Rheumatology. 2002;29(5):999–1005. - PubMed
-
- Kadir A. A., Ab Wahab S. Z., Zulkifli M. M., Noor N. M., Baie S. B. B., Haron J. The therapeutic effect of oral Channa striatus extract on primary knee osteoarthritis patients. Agro FOOD Industry Hi Tech. 2014;25(3):44–48.
-
- Somchit M. N., Solihah M. H., Israf D. A., Ahmad Z., Arifah A. K., Mat Jais A. M. Anti-inflammatiry activity of Channa striatus, Channa micropeltes and Channa lucius extract: chronic inflammatory modulation. Oriental Pharmacy and Experimental Medicine. 2004;4:91–94.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

