IL-27 and TCR Stimulation Promote T Cell Expression of Multiple Inhibitory Receptors
- PMID: 31356173
- PMCID: PMC6994206
- DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.1800083
IL-27 and TCR Stimulation Promote T Cell Expression of Multiple Inhibitory Receptors
Abstract
Inhibitory receptors (IR) are a diverse group of cell surface molecules that modulate T cell activation, but there are gaps in our knowledge of the cell-extrinsic factors that regulate their expression. The present study found that in vivo overexpression of IL-27 in mice led to increased T cell expression of PD-L1, LAG-3, TIGIT, and TIM-3. In vitro, TCR stimulation alone promoted expression of multiple IRs, whereas IL-27 alone induced expression of PD-L1. However, the combination of intermediate TCR stimulation and IL-27 resulted in synergistic induction of LAG-3, CTLA-4, and TIGIT. In vivo, infection with Toxoplasma gondii resulted in parasite-specific effector T cells that expressed high levels of IR, and at local sites of infection where IL-27 production was highest, IL-27 was required for maximal effector cell expression of PD-L1, LAG-3, CTLA-4, and TIGIT. Together, these results affirm the critical role of TCR signals in the induction of IR expression but find that during infection, IL-27 promotes T cell expression of IR.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
C.A.H. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board and Scientific Founder of Surface Oncology. The other authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
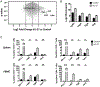




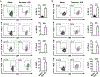

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

