The impact of APOE genotype on survival: Results of 38,537 participants from six population-based cohorts (E2-CHARGE)
- PMID: 31356640
- PMCID: PMC6663005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219668
The impact of APOE genotype on survival: Results of 38,537 participants from six population-based cohorts (E2-CHARGE)
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein E is a glycoprotein best known as a mediator and regulator of lipid transport and uptake. The APOE-ε4 allele has long been associated with increased risks of Alzheimer's disease and mortality, but the effect of the less prevalent APOE-ε2 allele on diseases in the elderly and survival remains elusive.
Methods: We aggregated data of 38,537 individuals of European ancestry (mean age 65.5 years; 55.6% women) from six population-based cohort studies (Rotterdam Study, AGES-Reykjavik Study, Cardiovascular Health Study, Health-ABC Study, and the family-based Framingham Heart Study and Long Life Family Study) to determine the association of APOE, and in particular APOE-ε2, with survival in the population.
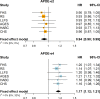
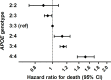
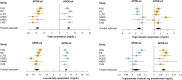
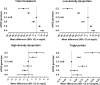
Results: During a mean follow-up of 11.7 years, 17,021 individuals died. Compared with homozygous APOE-ε3 carriers, APOE-ε2 carriers were at lower risk of death (hazard ratio,95% confidence interval: 0.94,0.90-0.99; P = 1.1*10-2), whereas APOE-ε4 carriers were at increased risk of death (HR 1.17,1.12-1.21; P = 2.8*10-16). APOE was associated with mortality risk in a dose-dependent manner, with risk estimates lowest for homozygous APOE-ε2 (HR 0.89,0.74-1.08), and highest for homozygous APOE-ε4 (HR 1.52,1.37-1.70). After censoring for dementia, effect estimates remained similar for APOE-ε2 (HR 0.95,0.90-1.01), but attenuated for APOE-ε4 (HR 1.07,1.01-1.12). Results were broadly similar across cohorts, and did not differ by age or sex. APOE genotype was associated with baseline lipid fractions (e.g. mean difference(95%CI) in LDL(mg/dL) for ε2 versus ε33: -17.1(-18.1-16.0), and ε4 versus ε33: +5.7(4.8;6.5)), but the association between APOE and mortality was unaltered after adjustment for baseline LDL or cardiovascular disease. Given the European ancestry of the study population, results may not apply to other ethnicities.
Conclusion: Compared with APOE-ε3, APOE-ε2 is associated with prolonged survival, whereas mortality risk is increased for APOE-ε4 carriers. Further collaborative efforts are needed to unravel the role of APOE and in particular APOE-ε2 in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Psaty serves on the DSMB for a clinical trial funded by Zoll LifeCor and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. None of the other authors report any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, Hyman B, Kukull WA, Mayeux R, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA. 1997. October;278(16):1349–56. - PubMed
-
- Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. February;13(2):397–406. 10.1074/mcp.M113.035600 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG023712/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG059421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG023122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG034424/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG051129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG043352/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061853/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD050374/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031287/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

