Mitochondrial oxidative stress-induced transcript variants of ATF3 mediate lipotoxic brain microvascular injury
- PMID: 31356870
- PMCID: PMC6848793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.024
Mitochondrial oxidative stress-induced transcript variants of ATF3 mediate lipotoxic brain microvascular injury
Abstract
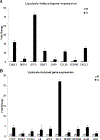
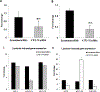
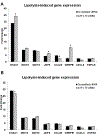
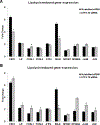
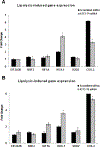
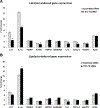
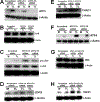
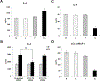
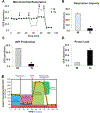
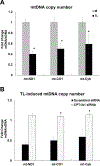
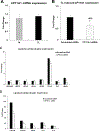
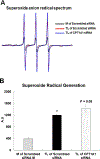
Elevation of blood triglycerides, primarily triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TGRL), is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease and vascular dementia (VaD). Accumulating evidence indicates that both atherosclerosis and VaD are linked to vascular inflammation. However, the role of TGRL in vascular inflammation, which increases risk for VaD, remains largely unknown and its underlying mechanisms are still unclear. We strived to determine the effects of postprandial TGRL exposure on brain microvascular endothelial cells, the potential risk factor of vascular inflammation, resulting in VaD. We showed in Aung et al., J Lipid Res., 2016 that postprandial TGRL lipolysis products (TL) activate mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increase the expression of the stress-responsive protein, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), which injures human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) in vitro. In this study, we deployed high-throughput sequencing (HTS)-based RNA sequencing methods and mito stress and glycolytic rate assays with an Agilent Seahorse XF analyzer and profiled the differential expression of transcripts, constructed signaling pathways, and measured mitochondrial respiration, ATP production, proton leak, and glycolysis of HBMECs treated with TL. Conclusions: TL potentiate ROS by mitochondria which activate mitochondrial oxidative stress, decrease ATP production, increase mitochondrial proton leak and glycolysis rate, and mitochondria DNA damage. Additionally, CPT1A1 siRNA knockdown suppresses oxidative stress and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and vascular inflammation in TL treated HBMECs. TL activates ATF3-MAPKinase, TNF, and NRF2 signaling pathways. Furthermore, the NRF2 signaling pathway which is upstream of the ATF3-MAPKinase signaling pathway, is also regulated by the mitochondrial oxidative stress. We are the first to report differential inflammatory characteristics of transcript variants 4 (ATF3-T4) and 5 (ATF3-T5) of the stress responsive gene ATF3 in HBMECs induced by postprandial TL. Specifically, our data indicates that ATF3-T4 predominantly regulates the TL-induced brain microvascular inflammation and TNF signaling. Both siRNAs of ATF3-T4 and ATF3-T5 suppress cells apoptosis and lipotoxic brain microvascular endothelial cells. These novel signaling pathways triggered by oxidative stress-responsive transcript variants, ATF3-T4 and ATF3-T5, in the brain microvascular inflammation induced by TGRL lipolysis products may contribute to pathophysiological processes of vascular dementia.
Keywords: Activating transcription factor 3; Brain microvascular endothelial cells; Inflammation; Lipolysis; Mitochondrial oxidative stress; RNA-Seq; Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ATF3 in atherosclerosis: a controversial transcription factor.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1557-1568. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02263-7. Epub 2022 Oct 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36207452 Review.
-
Induction of ATF3 gene network by triglyceride-rich lipoprotein lipolysis products increases vascular apoptosis and inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Sep;33(9):2088-96. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301375. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23868936 Free PMC article.
-
Lipotoxic brain microvascular injury is mediated by activating transcription factor 3-dependent inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways.J Lipid Res. 2016 Jun;57(6):955-68. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M061853. Epub 2016 Apr 17. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27087439 Free PMC article.
-
TGRL Lipolysis Products Induce Stress Protein ATF3 via the TGF-β Receptor Pathway in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 28;10(12):e0145523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145523. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26709509 Free PMC article.
-
Lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, vascular inflammation, and atherosclerosis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 May;1821(5):858-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.09.021. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22001233 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role of the itaconate-mediated rescue of cellular metabolic stress.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Sep 1;34(2):134-138. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_79_21. eCollection 2022 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 35465285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinically applied PARP inhibitor talazoparib ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice without reducing skin inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1519066. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1519066. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40046735 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylethanoid glycoside-enriched fraction of Clerodendrum glandulosum ameliorates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via PGC1α/TFAM upregulation.3 Biotech. 2025 Apr;15(4):85. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04235-3. Epub 2025 Mar 11. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40084243
-
ATF3 in atherosclerosis: a controversial transcription factor.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1557-1568. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02263-7. Epub 2022 Oct 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36207452 Review.
-
Irisin Rescues Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability following Traumatic Brain Injury and Contributes to the Neuroprotection of Exercise in Traumatic Brain Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 16;2021:1118981. doi: 10.1155/2021/1118981. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34697562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association, 2018 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures, Alzheimers Dement. 14 (2018) 367–429.
-
- Goldwaser EL, Acharya NK, Nagele RG, Cerebrovascular and Blood-Brain Barrier Compromise: A Mechanistic Link between Vascular Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease Subtypes of Neurocognitive Disorders, J Parkinsons Dis Alzheimer Dis. 2 (2015) 10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

