Perirenal fat thickness is associated with metabolic risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 31357262
- PMCID: PMC6727893
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.18.0155
Perirenal fat thickness is associated with metabolic risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Adipose tissue accumulation in specific body compartments has been associated with diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia. Perirenal fat (PRF) may lead to have direct lipotoxic effects on renal function and intrarenal hydrostatic pressure. This study was undertaken to explore the association of PRF with cardiovascular risk factors and different stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
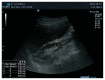
Methods: We studied 103 patients with CKD of different stages (1 to 5). PRF was measured by B-mode renal ultrasonography in the distal third between the cortex and the hepatic border and/or spleen.
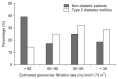
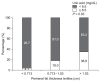
Results: The PRF thickness was greater in CKD patients with impaired fasting glucose than in those with normal glucose levels (1.10 ± 0.40 cm vs. 0.85 ± 0.39 cm, P < 0.01). Patients in CKD stages 4 and 5 (glomerular filtration rate [GFR] < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) had the highest PRF thickness. Serum triglyceride levels correlated positively with the PRF thickness; the PRF thickness was greater in patients with triglyceride levels ≥ 150 mg/dL (1.09 ± 0.40 cm vs. 0.86 ± 0.36 cm, P < 0.01). In patients with a GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, uric acid levels correlated positively with the PRF thickness (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In CKD patients, the PRF thickness correlated significantly with metabolic risk factors that could affect kidney function.
Keywords: Cardiovascular; Chronic kidney disease; Diabetes; Metabolic risk; Perirenal fat; Renal insufficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- KDIGO CKD Work Group. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1–150.
-
- Leavey SF, McCullough K, Hecking E, Goodkin D, Port FK, Young EW. Body mass index and mortality in ‘healthier’ as compared with ‘sicker’ haemodialysis patients: results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16:2386–2394. doi: 10.1093/ndt/16.12.2386. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

