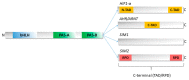
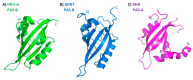
bHLH-PAS Proteins: Their Structure and Intrinsic Disorder
- PMID: 31357385
- PMCID: PMC6695611
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20153653
bHLH-PAS Proteins: Their Structure and Intrinsic Disorder
Abstract
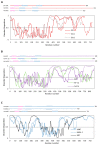
The basic helix-loop-helix/Per-ARNT-SIM (bHLH-PAS) proteins are a class of transcriptional regulators, commonly occurring in living organisms and highly conserved among vertebrates and invertebrates. These proteins exhibit a relatively well-conserved domain structure: the bHLH domain located at the N-terminus, followed by PAS-A and PAS-B domains. In contrast, their C-terminal fragments present significant variability in their primary structure and are unique for individual proteins. C-termini were shown to be responsible for the specific modulation of protein action. In this review, we present the current state of knowledge, based on NMR and X-ray analysis, concerning the structural properties of bHLH-PAS proteins. It is worth noting that all determined structures comprise only selected domains (bHLH and/or PAS). At the same time, substantial parts of proteins, comprising their long C-termini, have not been structurally characterized to date. Interestingly, these regions appear to be intrinsically disordered (IDRs) and are still a challenge to research. We aim to emphasize the significance of IDRs for the flexibility and function of bHLH-PAS proteins. Finally, we propose modern NMR methods for the structural characterization of the IDRs of bHLH-PAS proteins.
Keywords: C-terminus; IDR; bHLH–PAS transcription factor; intrinsically disordered region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
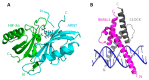

References
-
- Ema M., Hirota K., Mimura J., Abe H., Yodoi J., Sogawa K., Poellinger L., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Molecular mechanisms of transcription activation by HLF and HIF1alpha in response to hypoxia: Their stabilization and redox signal-induced interaction with CBP/p300. EMBO J. 1999;18:1905–1914. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.7.1905. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrulis J.R., Kusnadi A., Ramadoss P., Hollingshead B., Perdew G.H. The hsp90 Co-chaperone XAP2 Alters Importin β Recognition of the Bipartite Nuclear Localization Signal of the Ah Receptor and Represses Transcriptional Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:2677–2685. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209331200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

