'Low-Salt' Bread as an Important Component of a Pragmatic Reduced-Salt Diet for Lowering Blood Pressure in Adults with Elevated Blood Pressure
- PMID: 31357402
- PMCID: PMC6722563
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11081725
'Low-Salt' Bread as an Important Component of a Pragmatic Reduced-Salt Diet for Lowering Blood Pressure in Adults with Elevated Blood Pressure
Abstract
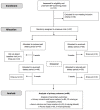
Reformulation of bread in terms of salt content remains an important measure to help achieve a reduction in salt intake in the population and for the prevention of hypertension and elevated blood pressure (BP). Our fundamental studies on the reduction of salt on dough and bread characteristics showed that wheat breads produced with 0.3 g salt/100 g ("low-salt") were found to be comparable quality to that produced with the typical level of salt (1.2%). This food-based intervention trial examined, using a 5 week cross-over design, the potential for inclusion of "low-salt" bread as part of a pragmatic reduced-salt diet on BP, markers of bone metabolism, and plasma lipids in 97 adults with slightly to moderately elevated BP. Assuming all sodium from dietary intake was excreted through the urine, the intake of salt decreased by 1.7 g/day, on average, during the reduced-salt dietary period. Systolic BP was significantly lower (by 3.3 mmHg on average; p < 0.0001) during the reduced-salt dietary period compared to the usual-salt dietary period, but there was no significant difference (p = 0.81) in diastolic BP. There were no significant differences (p > 0.12, in all cases) in any of the urinary- or serum-based biochemical indices of calcium or bone metabolism or in plasma lipids between the two periods. In conclusion, a modest reduction in dietary salt intake, in which the use of "low-salt" (i.e., 0.3 g/100g) bread played a key role along with dietary advice, and led to a significant, and clinically meaningful, decrease in systolic, but not diastolic, BP in adults with mildly to moderately elevated BP.
Keywords: blood pressure regulation; crossover trial; hypertension; low-salt bread; sodium restriction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Causes of Death in 2008. [(accessed on 4 February 2013)]; Available online: www.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/causes_death_2008/en/index.html.
-
- Mendis S., Puska P., Norrving B. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011. [(accessed on 4 February 2013)]. Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241564373_eng.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization . Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012. - PubMed
-
- Lim S.S., Vos T., Flaxman A.D., Danaei G., Shibuya K., Adair-Rohani H., Amann M., Anderson H.R., Andrews K.G., Aryee M., et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical