β-Amyrin Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease-Like Aberrant Synaptic Plasticity in the Mouse Hippocampus
- PMID: 31357749
- PMCID: PMC6939697
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.024
β-Amyrin Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease-Like Aberrant Synaptic Plasticity in the Mouse Hippocampus
Abstract
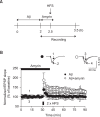
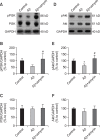
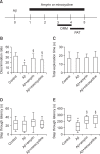
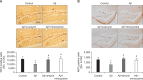
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive and most frequently diagnosed neurodegenerative disorder. However, there is still no drug preventing the progress of this disorder. β-Amyrin, an ingredient of the surface wax of tomato fruit and dandelion coffee, is previously reported to ameliorate memory impairment induced by cholinergic dysfunction. Therefore, we tested whether β-amyrin can prevent AD-like pathology. β-Amyrin blocked amyloid β (Aβ)-induced long-term potentiation (LTP) impairment in the hippocampal slices. Moreover, β-amyrin improved Aβ-induced suppression of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling. LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, blocked the effect of β-amyrin on Aβ-induced LTP impairment. In in vivo experiments, we observed that β-amyrin ameliorated object recognition memory deficit in Aβ-injected AD mice model. Moreover, neurogenesis impairments induced by Aβ was improved by β-amyrin treatment. Taken together, β-amyrin might be a good candidate of treatment or supplement for AD patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid β; Synaptic plasticity; β-amyrin.
Figures



References
-
- Arbel-Ornath M, Hudry E, Boivin JR, Hashimoto T, Takeda S, Kuchibhotla KV, Hou S, Lattarulo CR, Belcher AM, Shakerdge N, Trujillo PB, Muzikansky A, Betensky RA, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ. Soluble oligomeric amyloid-beta induces calcium dyshomeostasis that precedes synapse loss in the living mouse brain. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017;12:27. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0169-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

