Coordinated Control of rRNA Processing by RNA Polymerase I
- PMID: 31358304
- PMCID: PMC6744312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.07.002
Coordinated Control of rRNA Processing by RNA Polymerase I
Abstract
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is co- and post-transcriptionally processed into active ribosomes. This process is dynamically regulated by direct covalent modifications of the polymerase that synthesizes the rRNA, RNA polymerase I (Pol I), and by interactions with cofactors that influence initiation, elongation, and termination activities of Pol I. The rate of transcription elongation by Pol I directly influences processing of nascent rRNA, and changes in Pol I transcription rate result in alternative rRNA processing events that lead to cellular signaling alterations and stress. It is clear that in divergent species, there exists robust organization of nascent rRNA processing events during transcription elongation. This review evaluates the current state of our understanding of the complex relationship between transcription elongation and rRNA processing.
Keywords: RNA polymerase I; RNA processing; ribosome; transcription elongation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

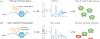
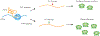

Similar articles
-
RNA polymerase II elongation factors Spt4p and Spt5p play roles in transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I and rRNA processing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 22;103(34):12707-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605686103. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16908835 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I is linked to efficient rRNA processing and ribosome assembly.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 27;26(2):217-29. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.007. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17466624 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk in gene expression: coupling and co-regulation of rDNA transcription, pre-ribosome assembly and pre-rRNA processing.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;17(3):281-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.04.001. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15901498 Review.
-
The RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) directly increases the elongation rate of RNA polymerase I and is required for efficient regulation of rRNA synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14152-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115220. Epub 2010 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20299458 Free PMC article.
-
Features of yeast RNA polymerase I with special consideration of the lobe binding subunits.Biol Chem. 2023 Oct 13;404(11-12):979-1002. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2023-0184. Print 2023 Oct 26. Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37823775 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Riboswitches Integrate Timescales for Bacterial Gene Expression Control.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jan 13;7:607158. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.607158. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33521053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excessive transcription-replication conflicts are a vulnerability of BRCA1-mutant cancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 22;51(9):4341-4362. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad172. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36928661 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RNA Polymerase I in Ewing Sarcoma Treatment.Cancer Sci. 2025 Aug;116(8):2317-2319. doi: 10.1111/cas.70047. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 40072351 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain of the A12.2 subunit stimulates RNA polymerase I transcription elongation.Biophys J. 2021 May 18;120(10):1883-1893. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.03.007. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33737158 Free PMC article.
-
Downstream sequence-dependent RNA cleavage and pausing by RNA polymerase I.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 31;295(5):1288-1299. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011354. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31843971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Initiative, A.G., Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana.nature, 2000. 408(6814): p. 796. - PubMed
-
- Herr AJ, et al., RNA Polymerase IV Directs Silencing of Endogenous DNA.Science, 2005. 308(5718): p. 118. - PubMed
-
- Provart NJ, et al., 50 years of Arabidopsis research: highlights and future directions.New Phytologist, 2016. 209(3): p. 921–944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

