Aberrant progranulin, YKL-40, cathepsin D and cathepsin S in Gaucher disease
- PMID: 31358474
- PMCID: PMC6864269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.07.014
Aberrant progranulin, YKL-40, cathepsin D and cathepsin S in Gaucher disease
Abstract
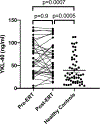
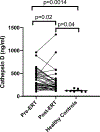
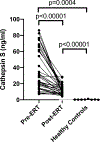
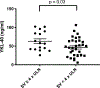
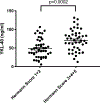
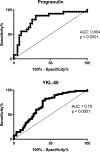
In Gaucher disease, several macrophage-specific biomarkers have been validated for use in the clinic. However, Gaucher disease is more complex involving system-wide pathophysiology beyond the macrophage, and based on gene array analysis in our Gaucher disease mouse model and other emerging pathophysiologic insights, we evaluated serum levels of cathepsins D and S, YKL-40 and progranulin in Gaucher disease patients. We assessed their biomarker potential in Gaucher disease and compared them to established Gaucher disease biomarkers, chitotriosidase, chemokine ligand 18 (CCL18), and other indicators of disease severity and response to therapy. Mean YKL-40 and cathepsin D and S levels were significantly higher in Gaucher disease patients compared to healthy controls; in contrast, mean progranulin levels were lower in Gaucher disease patients compared to healthy controls. Enzyme replacement therapy resulted in a significant reversal of elevated cathepsin D and S but there was no change in progranulin and YKL-40 levels. Patients with persistent splenomegaly after long-term enzyme replacement therapy had significantly higher serum YKL-40 than patients with smaller spleens (63.0 ± 6.4 ng/ml vs. 46.4 ± 4.3 ng/ml, p = .03). Serum YKL-40 levels were higher in subjects with severe bone involvement (Hermann Score 3 to 5) compared to those with milder bone involvement (Hermann Score 1 to 2) (70.1 ± 4.3 ng/ml vs. 48.1 ± 3.7 ng/ml, p = .0002). YKL-40 was only weakly associated with chitotriosidase (r = 0.2, p = .008) and CCL18 (r = 0.3, p = .0004), and cathepsin S was moderately associated with chitotriosidase (r = 0.4, p = .01) and CCL18 (r = 0.6, p < .0001). Receiver operating curves for progranulin and YKL-40 demonstrated areas under the curves of 0.80 and 0.70, respectively. In conclusion, while these biomarkers do not meet robust properties of established macrophage-specific biomarkers, they may inform severity of skeletal disease, contribution of fibrosis to residual splenomegaly, and other disease manifestations. These findings, including markedly low progranulin levels that do not change upon enzyme replacement therapy, are intriguing to prompt further investigations to decipher their role in pathophysiology and relevance to diverse phenotypes of Gaucher disease.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cathepsins; Gaucher disease; Progranulin; YKL-40.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Grabowski GA, Phenotype, diagnosis, and treatment of Gaucher’s disease. Lancet, 2008. 372(9645): p. 1263–71. - PubMed
-
- Boot RG, et al. , Marked elevation of the chemokine CCL18/PARC in Gaucher disease: a novel surrogate marker for assessing therapeutic intervention. Blood, 2004. 103(1): p. 33–9. - PubMed
-
- Khan A, et al. , Risk factors for fractures and avascular osteonecrosis in type 1 Gaucher disease: a study from the International Collaborative Gaucher Group (ICGG) Gaucher Registry. J Bone Miner Res, 2012. 27(8): p. 1839–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

