A semi-target analytical method for quantification of OH-PCBs in environmental samples
- PMID: 31359319
- PMCID: PMC6986979
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-05775-x
A semi-target analytical method for quantification of OH-PCBs in environmental samples
Abstract
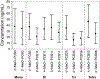
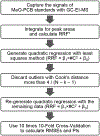
Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls (OH-PCBs) are oxidative metabolites of PCBs and residuals found in original Aroclors. OH-PCBs are known to play a role as genotoxicants, carcinogens, and hormone disruptors, and therefore it is important to quantify their presence in human tissues, organisms, and environmental matrices. Of 837 possible mono-OH-PCBs congeners, there are only ~ 70 methoxylated PCB (MeO-PCB) standards commercially available. Hence, a semi-target analytical method is needed for unknown OH-PCBs. The mass concentrations of these unknowns are sometimes determined by assuming the peak responses of other available compounds. This can bias the results due to the choices and availabilities of standards. To overcome this issue, we investigated the peak responses of all commercially available MeO-PCB standards with gas chromatography (GC) coupling with triple quadrupole (QqQ) mass spectrometry (MS) system, with positive electron impact (EI) ionization at 20-70 eV in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. We found correlations between the relative peak responses (RRFs) and the number of chlorine (#Cl) in the molecules of MeO-PCBs. Among the studied models, the quadratic regression of #Cl is the most suitable model in the RRF prediction (RRF = β1 × #Cl^2 + β0) when the peak responses are captured at 30 eV. We evaluated the performance of the model by analyzing 12 synthesized MeO-PCB standards and a PCB-contaminated sediment collected from a wastewater lagoon. We further demonstrate the utility of the model using a different chromatography column and GC-EI-MS system. We found the method and associated model to be sufficiently simple, accurate, and versatile for use in quantifying OH-PCBs in complex environmental samples.
Keywords: Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls; OH-PCBs; Quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Machine Learning-Assisted Identification and Quantification of Hydroxylated Metabolites of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Animal Samples.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Sep 20;56(18):13169-13178. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c02027. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36047920 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxylated Polychlorinated Biphenyls Are Emerging Legacy Pollutants in Contaminated Sediments.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Feb 15;56(4):2269-2278. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c04780. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35107261 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls (OH-PCBs) in sediment from a lake Michigan waterway and original commercial aroclors.Environ Sci Technol. 2013 Aug 6;47(15):8204-10. doi: 10.1021/es402323c. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Environ Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23862721 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical approaches for the determination of PCB metabolites in blood: a review.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Oct;406(25):6151-64. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-7922-5. Epub 2014 Jun 8. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24908411 Review.
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment.Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994;24(2):87-149. doi: 10.3109/10408449409049308. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994. PMID: 8037844 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning-Assisted Identification and Quantification of Hydroxylated Metabolites of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Animal Samples.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Sep 20;56(18):13169-13178. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c02027. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36047920 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of mono- and dimethoxylated polychlorinated biphenyl derivatives starting from fluoroarene derivatives.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Mar;27(9):8905-8925. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07133-3. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31893358 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxylated Polychlorinated Biphenyls Are Emerging Legacy Pollutants in Contaminated Sediments.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Feb 15;56(4):2269-2278. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c04780. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35107261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2000) Toxicological Profile for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs). U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Atlanta, GA, USA - PubMed
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2011) Addendum to the Toxicological Profile for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs). U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Atlanta, GA, USA - PubMed
-
- Amano I, Miyazaki W, Iwasaki T, Shimokawa N, Koibuchi N (2010) The effect of hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyl (OH-PCB) on thyroid hormone receptor (TR)-mediated transcription through native-thyroid hormone response element (TRE) Industrial health 48:115–118 - PubMed
-
- American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA) (2013) White Paper Examines the Potential Hazards of PCBs in the Building Environment Falls Church, VA, USA
-
- Anderson PN, Hites RA (1996) OH Radical Reactions: The Major Removal Pathway for Polychlorinated Biphenyls from the Atmosphere Environmental Science & Technology 30:1756–1763 doi:10.1021/es950765k - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

