An evaluation of sequencing coverage and genotyping strategies to assess neutral and adaptive diversity
- PMID: 31359622
- PMCID: PMC7115901
- DOI: 10.1111/1755-0998.13070
An evaluation of sequencing coverage and genotyping strategies to assess neutral and adaptive diversity
Abstract
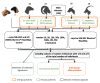
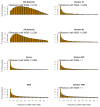
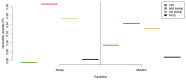
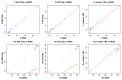
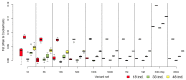
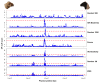
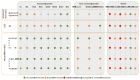
Whole genome sequences (WGS) greatly increase our ability to precisely infer population genetic parameters, demographic processes, and selection signatures. However, WGS may still be not affordable for a representative number of individuals/populations. In this context, our goal was to assess the efficiency of several SNP genotyping strategies by testing their ability to accurately estimate parameters describing neutral diversity and to detect signatures of selection. We analysed 110 WGS at 12× coverage for four different species, i.e., sheep, goats and their wild counterparts. From these data we generated 946 data sets corresponding to random panels of 1K to 5M variants, commercial SNP chips and exome capture, for sample sizes of five to 48 individuals. We also extracted low-coverage genome resequencing of 1×, 2× and 5× by randomly subsampling reads from the 12× resequencing data. Globally, 5K to 10K random variants were enough for an accurate estimation of genome diversity. Conversely, commercial panels and exome capture displayed strong ascertainment biases. Besides the characterization of neutral diversity, the detection of the signature of selection and the accurate estimation of linkage disequilibrium (LD) required high-density panels of at least 1M variants. Finally, genotype likelihoods increased the quality of variant calling from low coverage resequencing but proportions of incorrect genotypes remained substantial, especially for heterozygote sites. Whole genome resequencing coverage of at least 5× appeared to be necessary for accurate assessment of genomic variations. These results have implications for studies seeking to deploy low-density SNP collections or genome scans across genetically diverse populations/species showing similar genetic characteristics and patterns of LD decay for a wide variety of purposes.
Keywords: SNP chip; depth of coverage; genotyping-by-sequencing; mammals; population genomics; whole genome sequencing.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

