Effect of acupuncture at ST36 on motor cortical excitation and inhibition
- PMID: 31359627
- PMCID: PMC6749473
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1370
Effect of acupuncture at ST36 on motor cortical excitation and inhibition
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) is often used to facilitate motor recovery after stroke. However, the effect of acupuncture at ST36 on motor cortical excitation and inhibition remains unclear. This study aimed to explore the effect of acupuncture at ST36 on motor cortical excitation and inhibition.
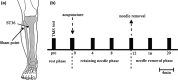
Methods: Twenty healthy volunteers were recruited to receive acupuncture treatment. We selected the acupoint ST36 and its respective sham point as the experimental acupoint. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) was used to measure motor-evoked potentials (MEP) at 7 time points-before acupuncture (Pre), acupuncture (T0), 4 and 8 min after acupuncture (T4; T8), needle removal (T12), 4 and 8 min after needle removal (T16; T20). Simultaneously, paired TMS (pTMS) was employed to measure short- and long-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI [short latency intracortical inhibition]; LICI [long latency intracortical inhibition]), respectively, at three time points-before acupuncture (Pre), acupuncture (T0), needle removal (T12). After removing the acupuncture needle, all subjects were asked to quantify their Deqi sensation using a Gas table.
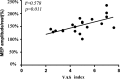
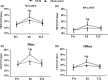
Results: The average Deqi sensation score of all subjects during acupuncture at ST36 was higher than that observed at the sham point. With acupuncture at ST36, the MEP amplitude was higher at three time points (T0, T4, T8) than at Pre, although the MEP amplitude tended toward Pre after needle removal. The MEP amplitude was also higher at the same time points (T0, T4, T8) than at the sham point. Furthermore, the Deqi sensation score was correlated with MEP amplitude. With acupuncture at ST36, SICI and LICI at T0 were higher than those at Pre, and SICI and LICI at T0 were higher than those at the sham point.
Conclusion: Acupuncture at ST36 increased motor cortical excitation and had an effect on the remaining needle phase. Deqi sensation was correlated with MEP amplitude. Acupuncture at ST36 also decreased motor cortical inhibition.
Keywords: Deqi; ST36; long-interval intracortical inhibition; motor-evoked potential; short-interval intracortical inhibition; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
© 2019 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Geng, W.‐Y. , Liu, Z.‐B. , Song, N.‐N. , Zhang, G.‐H. , Jin, W.‐Z. , Zhou, W. , … Shen, L.‐L. (2013). Effects of electroacupuncture at zusanli (st36) on inflammatory cytokines in a rat model of smoke‐induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of Integrative Medicine, 11(3), 213–219. 10.3736/jintegrmed2013024 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

