Correlation of EYS polymorphisms with lumbar disc herniation risk among Han Chinese population
- PMID: 31359629
- PMCID: PMC6732306
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.890
Correlation of EYS polymorphisms with lumbar disc herniation risk among Han Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a common spinal disease in clinical practice. Once lumbar disc herniation occurs, it seriously reduces patient's quality of life. The EYS (eyes shut homolog) was discovered in recent years and it may be related to lumbar disc herniation. So we conducted a case-control study to explore the relationship between EYS polymorphism and lumbar disc herniation risk.
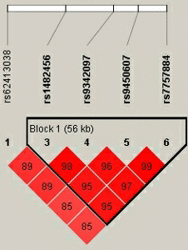
Methods: We selected 5 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of EYS gene in a case-control study with 508 cases and 508 healthy controls to evaluate the relatedness by using genetic model, haplotype, and stratification analysis.
Results: We found that the minor alleles of rs62413038 (OR = 1.21, 95%CI: 1.01-1.43, p = .036) and rs9450607 (OR = 1.26, 95% CI: 1.05-1.53, p = .016) were associated with an increased risk of lumbar disc herniation in the allelic model analysis. In the genotypic model analysis, rs62413038 displayed a significantly increased risk of lumbar disc herniation in log-additive models (OR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.01-1.43, p = .039). While the rs9450607 was also obviously associated with an increased lumbar disc herniation risk in recessive (OR = 1.98, 95% CI: 1.24-3.13, p = .004) and log-additive models (OR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.05-1.55, p = .014). In addition, in the haplotype analyses of the SNPs, we found that the "CGGA" haplotype of rs1482456, rs9342097, rs9450607, and rs7757884 was associated with lumbar disc herniation. (OR = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.30-0.89, p = .017).
Conclusion: These results suggest that EYS polymorphism may be associated with lumbar disc herniation among Han Chinese population. It also opens up a new exploration direction for the etiology of lumbar disc herniation.
Keywords: EYS; Case-control study; Lumbar disc herniation (LDH); Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
© 2019 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Casa, N. L. , Casa Junior, A. J. , Melo, A. V. , Teodoro, L. S. , Nascimento, G. R. , Sousa, A. F. , … Curado, M. P. (2016). CASE‐REPORT Association between an ACAN gene variable number tandem repeat polymorphism and lumbar disc herniation: A case control study. Genetics and Molecular Research, 15, 10.4238/gmr15048867 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fuchs, O. , Gorlanova, O. , Latzin, P. , Schmidt, A. , Schieck, M. , Toncheva, A. A. , … Frey, U. (2017). 6q12 and 11p14 variants are associated with postnatal exhaled nitric oxide levels and respiratory symptoms. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 140, 1015–1023. 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.11.048 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical