Behavior Modification Maintenance with Long-Term Blood Glucose and Weight Management in Prader-Willi Syndrome Complicated with Diabetes: Team Management Approach Combined with Pharmacological Treatment
- PMID: 31360171
- PMCID: PMC6644266
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6129019
Behavior Modification Maintenance with Long-Term Blood Glucose and Weight Management in Prader-Willi Syndrome Complicated with Diabetes: Team Management Approach Combined with Pharmacological Treatment
Abstract
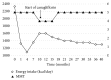
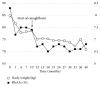
The patient was a 40-year-old woman, who had been diagnosed with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) at 1 year of age and type 2 diabetes at 27 years of age. At 34 years of age, she was hospitalized to start insulin therapy and receive guidance on treatment. During the next 6 months and through regular once-monthly outpatient clinic visits, the blood glucose level was relatively stabilized although body weight gradually increased. Two years following discharge, the blood glucose level became unstable, and she was hospitalized again to receive guidance on treatment. A team medicine-based approach was established upon hospitalization. The basic treatment was unchanged (insulin, diet, and exercise). The approach taken by the team included understanding the characteristics of PWS by all team members, clear definition of treatment goals, positive evaluation of the patient, and maintenance of the patient's motivation for treatment. Anxiety and stress related to mother's illness dampened motivation and adherence to treatment, but the addition of appropriate pharmacological treatment helped in rapid recovery of motivation to adhere to the treatment protocol. At 3 years after discharge, HbA1c is maintained at around 6%, and body weight continues to fall. Our protocol of the combination of a team medicine approach with appropriately timed pharmacological intervention could probably be applied to not only type 2 diabetes in PWS but also the management of patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Update on Diabetes Mellitus and Glucose Metabolism Alterations in Prader-Willi Syndrome.Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Feb 6;20(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-1284-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32030506 Review.
-
Effectiveness of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor as an Add-on Drug to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Glycemic Control of a Patient with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Case Report.Diabetes Ther. 2018 Feb;9(1):421-426. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0369-5. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Diabetes Ther. 2018. PMID: 29335890 Free PMC article.
-
The behavioral impact of growth hormone treatment for children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome: a 2-year, controlled study.Pediatrics. 2002 Feb;109(2):E35. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.2.e35. Pediatrics. 2002. PMID: 11826245 Clinical Trial.
-
A comprehensive team approach to the management of patients with Prader-Willi syndrome.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Sep;17(9):1153-75. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2004.17.9.1153. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15506675 Review.
-
Physiological adaptation after a 12-week physical activity program for patients with Prader-Willi syndrome: two case reports.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Jun 23;10(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0966-8. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27339289 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Diet Quality and Nutritional State of Children, Youth, and Young Adults with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Polish Multiple Case Study.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 31;15(17):3811. doi: 10.3390/nu15173811. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686843 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity in Prader-Willi syndrome: physiopathological mechanisms, nutritional and pharmacological approaches.J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Oct;44(10):2057-2070. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01574-9. Epub 2021 Apr 23. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021. PMID: 33891302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on Diabetes Mellitus and Glucose Metabolism Alterations in Prader-Willi Syndrome.Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Feb 6;20(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-1284-5. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32030506 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

