Bio-based building blocks from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural via 1-hydroxyhexane-2,5-dione as intermediate
- PMID: 31360410
- PMCID: PMC6585594
- DOI: 10.1039/c9sc01309a
Bio-based building blocks from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural via 1-hydroxyhexane-2,5-dione as intermediate
Abstract
The limits to the supply of fossil resources and their ever increasing use forces us to think about future scenarios for fuels and chemicals. The platform chemical 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural (HMF) can be obtained from biomass in good yield and has the potential to be converted in just a few steps into a multitude of interesting products. Over the last 20 years, the conversion of HMF to 1-hydroxyhexane-2,5-dione (HHD) has been studied by several groups. It is possible to convert HMF into HHD by hydrogenation/hydrolytic ring opening reaction in aqueous phase using various heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts. This review addresses both the state of the art of HHD synthesis, including mechanistic aspects of its formation, as well as the recent progress in the application of HHD as a building block for many useful chemicals including pyrroles, cyclopentanone derivatives and triols.
Figures

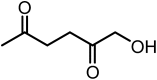



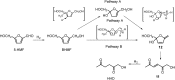








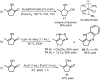







References
-
- Rubio Rodriguez M. A., De Ruyck J., Roque Diaz P., Verma V. K., Bram S. Appl. Energy. 2011;88:630–635.
-
- Nel W. P., Cooper C. J. Energy Policy. 2009;37:166–180.
-
- Shafiee S., Topal E. Energy Policy. 2009;37:181–189.
-
- Kamm B., Gruber P. R. and Kamm M., Biorefineries: Industrial Processes and Products, in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2012.
-
- Werpy T. and Petersen G., Top Value-Added Chemicals from Biomass, Vol. I: Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Sugars and Synthesis Gas, U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, 2004.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

