Is it necessary to show virtual limbs in action observation neurorehabilitation systems?
- PMID: 31360538
- PMCID: PMC6636217
- DOI: 10.1177/2055668319859140
Is it necessary to show virtual limbs in action observation neurorehabilitation systems?
Abstract
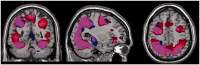
Introduction: Action observation neurorehabilitation systems are usually based on the observation of a virtual limb performing different kinds of actions. In this way, the activity in the frontoparietal Mirror Neuron System is enhanced, which can be helpful to rehabilitate stroke patients. However, the presence of limbs in such systems might not be necessary to produce mirror activity, for example, frontoparietal mirror activity can be produced just by the observation of virtual tool movements. The objective of this work was to explore to what point the presence of a virtual limb impacts the Mirror Neuron System activity in neurorehabilitation systems.
Methods: The study was conducted by using an action observation neurorehabilitation task during a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) experiment with healthy volunteers and comparing two action observation conditions that: 1 - included or 2 - did not include a virtual limb.
Results: It was found that activity in the Mirror Neuron System was similar during both conditions (i.e. virtual limb present or absent).
Conclusions: These results open up the possibility of using new tasks that do not include virtual limbs in action observation neurorehabilitation environments, which can give more freedom to develop such systems.
Keywords: action observation; fMRI; mirror neurons; neurorehabilitation; virtual limbs; virtual reality.
Figures
References
-
- Dipellegrino G, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, et al. Understanding motor events: a neurophysiological study. Exp Brain Res 1992; 91: 176–180. - PubMed
-
- Gallese V, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, et al. Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain 1996; 119: 593–609. - PubMed
-
- Gallese V, Fadiga L, Fogassi L, et al. Action representation and the inferior parietal lobule. Common Mech Percept Action 2002; 19: 334–355.
-
- Cattaneo L, Rizzolatti G. The Mirror Neuron System. Arch Neurol 2009; 66: 557–560. - PubMed
-
- Brihmat N, Tarri M, Quide Y, et al. Action, observation or imitation of virtual hand movement affect differently regions of the mirror neuron system and the default mode network. Brain Imaging Behav 2018; 12: 1363–1378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

