Premorbid Adjustment and IQ in Patients With First-Episode Psychosis: A Multisite Case-Control Study of Their Relationship With Cannabis Use
- PMID: 31361020
- PMCID: PMC7147569
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbz077
Premorbid Adjustment and IQ in Patients With First-Episode Psychosis: A Multisite Case-Control Study of Their Relationship With Cannabis Use
Abstract
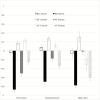
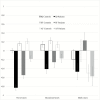
Psychotic patients with a lifetime history of cannabis use generally show better cognitive functioning than other psychotic patients. Some authors suggest that cannabis-using patients may have been less cognitively impaired and less socially withdrawn in their premorbid life. Using a dataset comprising 948 patients with first-episode psychosis (FEP) and 1313 population controls across 6 countries, we examined the extent to which IQ and both early academic (Academic Factor [AF]) and social adjustment (Social Factor [SF]) are related to the lifetime frequency of cannabis use in both patients and controls. We expected a higher IQ and a better premorbid social adjustment in psychotic patients who had ever used cannabis compared to patients without any history of use. We did not expect such differences in controls. In both patients and controls, IQ was 3 points higher among occasional-users than in never-users (mean difference [Mdiff] = 2.9, 95% CI = [1.2, 4.7]). Both cases and control daily-users had lower AF compared to occasional (Mdiff = -0.3, 95% CI = [-0.5; -0.2]) and never-users (Mdiff = -0.4, 95% CI = [-0.6; -0.2]). Finally, patient occasional (Mdiff = 0.3, 95% CI = [0.1; 0.5]) and daily-users (Mdiff = 0.4, 95% CI = [0.2; 0.6]) had better SF than their never-using counterparts. This difference was not present in controls (Fgroup*frequency(2, 2205) = 4.995, P = .007). Our findings suggest that the better premorbid social functioning of FEP with a history of cannabis use may have contributed to their likelihood to begin using cannabis, exposing them to its reported risk-increasing effects for Psychotic Disorders.
Keywords: cognition; education; marijuana; preillness; schizophrenia; sociability.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Gage SH, Hickman M, Zammit S. Association between cannabis and psychosis: epidemiologic evidence. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(7):549–556. - PubMed
-
- Moore TH, Zammit S, Lingford-Hughes A, et al. . Cannabis use and risk of psychotic or affective mental health outcomes: a systematic review. Lancet. 2007;370(9584):319–328. - PubMed
-
- Potvin S, Amar MB. Review: cannabis use increases the risk of psychotic outcomes. Evid Based Ment Health. 2008;11(1):28. - PubMed
-
- Grant I, Gonzalez R, Carey CL, Natarajan L, Wolfson T. Non-acute (residual) neurocognitive effects of cannabis use: a meta-analytic study. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2003;9(5):679–689. - PubMed
-
- Schreiner AM, Dunn ME. Residual effects of cannabis use on neurocognitive performance after prolonged abstinence: a meta-analysis. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012;20(5):420–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

