Alloimmunization of a dog erythrocyte antigen 1- dog transfused with weakly dog erythrocyte antigen 1+ blood
- PMID: 31361062
- PMCID: PMC6766507
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.15565
Alloimmunization of a dog erythrocyte antigen 1- dog transfused with weakly dog erythrocyte antigen 1+ blood
Abstract
Background: Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions because of dog erythrocyte antigen (DEA) 1 sensitization after mismatched transfusions are serious complications. Dog erythrocyte antigen 1 expression varies from negative to weakly to strongly positive.
Objectives: To assess alloimmunization after transfusion of weakly DEA 1+ blood to a DEA 1- dog.
Animals: One DEA 1- recipient and 1 weakly DEA 1+ donor, and 106 control dogs.
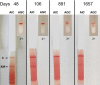
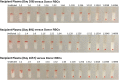
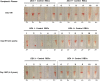
Methods: Long-term follow-up study. Matched for DEA 3, 4, 5, and 7, Dal, and Kai 1 and 2, weakly DEA 1+ donor packed red blood cells (RBCs) were transfused 3 times (0.45 mL/kg at Day 0, 16, and 37) to a DEA 1- recipient. Alloantibodies against RBCs from donor and 106 controls were determined in recipient's plasma samples using a commercial antiglobulin-enhanced immunochromatographic strip and gel tube crossmatches. Alloantibody titers were determined.
Results: The DEA 1- recipient was sensitized after 16 days to ≥1657 days after transfusion to weakly DEA 1+ and otherwise matched RBCs. Strong to moderate crossmatch incompatibilities were observed between recipient's plasma and all 61 DEA 1+ crossmatched controls. Moderate to weak incompatibilities were also observed to DEA 1- controls. Anti-DEA 1 and other alloantibodies were detected over the 4.5 year observation period.
Conclusions and clinical importance: Blood from a weakly DEA 1+ donor induces a strong and durable alloimmunization in a DEA 1- recipient dog. Additional alloantibodies developed against yet to be defined RBC antigens. Those results support the recommendation of typing dogs against DEA 1, considering weakly DEA 1+ as immunogenic, and crossmatching all previously transfused dogs.
Keywords: alloantibodies; blood compatibility; canine; dog erythrocyte antigen; hemolytic transfusion reaction.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Guidetti was employed, and I. Goy‐Thollot and U. Giger have been scientific advisors to Dianov. Reagents, commercial typing and crossmatch kits were provided for these studies by Alvedia. The design and execution of the study, data analysis, and writing of the manuscript have been done independently. U. Giger is the director of PennGen at the University of Pennsylvania which is a non‐for‐profit laboratory offering blood typing and compatibility testing.
Figures



References
-
- Andrews GA, Chavey PS, Smith JE. Production, characterization, and applications of a murine monoclonal antibody to dog erythrocyte antigen 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1992;201(10):1549‐1552. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
