Irreversible oxidative post-translational modifications in heart disease
- PMID: 31361162
- PMCID: PMC6816499
- DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2019.1645602
Irreversible oxidative post-translational modifications in heart disease
Abstract
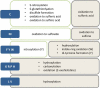
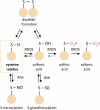
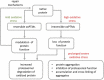
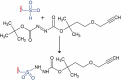
Introduction: Development of specific biomarkers aiding early diagnosis of heart failure is an ongoing challenge. Biomarkers commonly used in clinical routine usually act as readouts of an already existing acute condition rather than disease initiation. Functional decline of cardiac muscle is greatly aggravated by increased oxidative stress and damage of proteins. Oxidative post-translational modifications occur already at early stages of tissue damage and are thus regarded as potential up-coming disease markers. Areas covered: Clinical practice regarding commonly used biomarkers for heart disease is briefly summarized. The types of oxidative post-translational modification in cardiac pathologies are discussed with a special focus on available quantitative techniques and characteristics of individual modifications with regard to their stability and analytical accessibility. As irreversible oxidative modifications trigger protein degradation pathways or cause protein aggregation, both influencing biomarker abundance, a chapter is dedicated to their regulation in the heart.
Keywords: Heart failure; oxidative stress; post-translational modifications; protein aggregation; protein degradation.
Figures
References
-
- Mailloux RJ, McBride SL, Harper ME. Unearthing the secrets of mitochondrial ROS and glutathione in bioenergetics. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013;38(12):592–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
