Fractures and their sequelae in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: the Stockholm CREAtinine Measurement project
- PMID: 31361316
- PMCID: PMC7643673
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfz142
Fractures and their sequelae in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: the Stockholm CREAtinine Measurement project
Abstract
Introduction: People undergoing maintenance dialysis are at high risk for fractures, but less is known about fracture incidence and associated outcomes in earlier stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods: We conducted an observational analysis from the Stockholm Creatinine Measurement project, a Swedish health care utilization cohort during 2006-11. We identified all adults with confirmed CKD Stages 3-5 and no documented history of fractures and extracted information on comorbid history, ongoing medication, cardiovascular events and death. We studied incidence rates of fractures (overall and by location), with the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) as time-dependent exposure. We then studied hazard ratios [HRs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs)] for the events of death and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) using Cox regression with fracture as time-varying exposure.
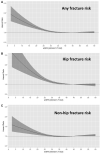
Results: We identified 68 764 individuals with confirmed CKD (mean age 79 years, 56% women). During a median follow-up of 2.7 years, 9219 fractures occurred, of which 3105 were hip fractures. A more severe CKD stage was associated with a higher risk of fractures, particularly hip fractures: compared with CKD Stage 3a, the adjusted HR was 1.10 (95% CI 1.02-1.19), 1.32 (1.17-1.49) and 2.47 (1.94-3.15) for CKD Stage 3b, 4 and 5, respectively. Spline curves suggested a linear association with fracture risk with an eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Compared with non-fracture periods, incident fracture was associated with a 4-fold increased mortality within 90 days [HR 4.21 (95% CI 3.95-4.49)]. The risk remained elevated beyond 90 days [HR 1.47 (95% CI 1.40-1.54)] and was stronger after hip fractures. Post-fracture MACE risk was also highest in the first 90 days [HR 4.02 (95% CI 3.73-4.33)], particularly after hip fractures, and persisted beyond 90 days [HR 1.20 (95% CI 1.10-1.30)].
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the commonness of fractures and the increased risk for subsequent adverse outcomes in CKD patients. These results may inform clinical decisions regarding post-fracture clinical surveillance and fracture prevention strategies.
Keywords: cardiovascular events; chronic kidney disease; epidemiology; fractures; mineral bone disorder.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Llach F. Secondary hyperparathyroidism in renal failure: the trade-off hypothesis revisited. Am J Kidney Dis 1995; 25: 663–679 - PubMed
-
- Moe S, Drueke T, Cunningham J et al. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int 2006; 69: 1945–1953 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous