Considering the child welfare system burden from opioid misuse: research priorities for estimating public costs
- PMID: 31361428
- PMCID: PMC7895335
Considering the child welfare system burden from opioid misuse: research priorities for estimating public costs
Abstract
The negative impact of opioids on those who misuse them has been widely documented. Despite significant spillover effects in the form of elevated rates of child maltreatment and child welfare system (CWS) involvement for children affected by parental opioid misuse, the public costs of opioid misuse to the CWS remain largely undocumented. This work seeks to understand the value and limitations of public data in estimating the costs of the opioid epidemic on the CWS. National data from federal sources are combined with best estimates of the association between opioid misuse and child services system utilization. The limitations of this work are explored, and future research priorities are outlined. Ultimately, this work illustrates the need to (1) improve data quality related to parental opioid misuse and CWS linkages; (2) better estimate the number of children and families coming into contact with the CWS as a result of parental opioid misuse; (3) improve predictions of CWS trajectories, including investigation, service provision, and foster care entry among this population; and (4) better estimate the CWS costs associated with patterns of system involvement resulting from parental opioid misuse. This information is crucial to ensuring the production of high-quality system involvement and cost projections related to the opioid crisis.
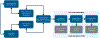
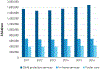
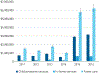
Figures

References
-
- Rudd RA, Aleshire N, Zibbell JE, Gladden RM. Increases in drug and opioid overdose deaths—United States, 2000–2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;64(50–51):1378–1382. - PubMed
-
- Murthy VH. Ending the opioid epidemic — a call to action. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(25):2413–2415. - PubMed
-
- Skolnick P The opioid epidemic: crisis and solutions. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;58:143–159. - PubMed
-
- Leslie DL, Ba DM, Agbese E, Xing X, Liu G. The economic burden of the opioid epidemic on states: the case of Medicaid. Am J Manag Care. 2019;25:S243–S249. - PubMed
