Response of seedling growth and physiology of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench to saline-alkali stress
- PMID: 31361760
- PMCID: PMC6667135
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220340
Response of seedling growth and physiology of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench to saline-alkali stress
Abstract
Soil salinization is a serious problem that affects the seedling growth in many regions. A greenhouse experiment was carried to investigate the adaptation ability of seedlings (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench.) in coastal saline alkaline environment. Seedlings of sorghum were treated by different salt and alkali stress (NaCl: Na2SO4: NaHCO3 were 2:1:0, 2:1:1, 2:1:2). The treatments consisted of three levels of salinity (100, 200 and 300 mmol/L) and pH values were 7.08, 8.78 and 9.04. The results showed that the seedlings of sorghum have good adaptability to salt stress under low pH (pH ≤7.08). The plant height, the maximum leave areas of seedlings all dropped and root length first ascended and then descended with the increasing of salt and alkali stress. The contents of Chlorophyll b degraded significantly under salt and alkali stress. Salt and alkali stress stimulated the accumulation of organic solutes (proline and protein) and inorganic ions (Na+, Cl-, SO42-). Our results showed that salt and alkali stress have significant effect on growth indexes except root length and the interaction effect has significantly on physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

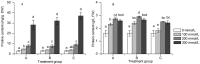

References
-
- Song J., Fan H., Zhao Y.Y., Jia Y.H., Du X.H., Wang B.S. Effect of salinity on germination, seedling emergence, seedling growth and ion accumulation of a euhalophyte Suaeda salsa in an intertidal zone and on saline inland. Aquatic Botany. 2008;88: 331–337.
-
- Shi D.C., Sheng Y.M. Effect of various salt–alkaline mixed stress conditions on sunflower seedlings and analysis of their stress factors. Environmental and Experimental Botany. 2005;54: 8–21.
-
- Wang X.P., Geng S.J., Ri Y.J., Cao D.H., Liu J., Shi D.C., Yang C.W. Physiological responses and adaptive strategies of tomato plants to salt and alkali stresses. Scientia Horticulturae. 2011;130: 248–255.
-
- Ashraf M. Some important physiological selection criteria for salt tolerance in plants. Flora—Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants.2004;199: 361–376.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

