TET1 regulates fibroblast growth factor 8 transcription in gonadotropin releasing hormone neurons
- PMID: 31361780
- PMCID: PMC6667164
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220530
TET1 regulates fibroblast growth factor 8 transcription in gonadotropin releasing hormone neurons
Abstract
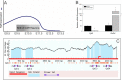
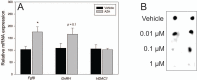
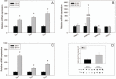
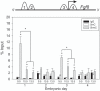
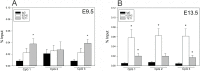
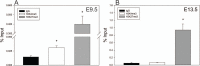
Fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) is a potent morphogen that regulates the ontogenesis of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons, which control the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, and therefore reproductive success. Indeed, FGF8 and FGFR1 deficiency severely compromises vertebrate reproduction in mice and humans and is associated with Kallmann Syndrome (KS), a congenital disease characterized by hypogonadotropic hypogonadism associated with anosmia. Our laboratory demonstrated that FGF8 signaling through FGFR1, both of which are KS-related genes, is necessary for proper GnRH neuron development in mice and humans. Here, we investigated the possibility that non-genetic factors, such as the epigenome, may contribute to KS onset. For this purpose, we developed an embryonic explant model, utilizing the mouse olfactory placode (OP), the birthplace of GnRH neurons. We show that TET1, which converts 5-methylcytosine residues (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylated cytosines (5hmC), controls transcription of Fgf8 during GnRH neuron ontogenesis. Through MeDIP and ChIP RT-qPCR we found that TET1 bound to specific CpG islands on the Fgf8 promoter. We found that the temporal expression of Fgf8 correlates with not only TET1 binding, but also with 5hmC enrichment. siRNA knockdown of Tet1 reduced Fgf8 and Fgfr1 mRNA expression. During this time period, Fgf8 also switched histone status, most likely via recruitment of EZH2, a major component of the polycomb repressor complex-2 (PRC2) at E13.5. Together, these studies underscore the significance of epigenetics and chromatin modifications to temporally regulated genes involved in KS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Compound deficiencies in multiple fibroblast growth factor signalling components differentially impact the murine gonadotrophin-releasing hormone system.J Neuroendocrinol. 2010 Aug;22(8):944-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02024.x. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Neuroendocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20553372 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased FGF8 signaling causes deficiency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in humans and mice.J Clin Invest. 2008 Aug;118(8):2822-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI34538. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18596921 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic control of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurone development and hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism.J Neuroendocrinol. 2020 Jun;32(6):e12860. doi: 10.1111/jne.12860. Epub 2020 May 26. J Neuroendocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32452569 Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis identifies a functional association of Tet1 and Polycomb repressive complex 2 in mouse embryonic stem cells.Genome Biol. 2013 Aug 29;14(8):R91. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-8-r91. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23987249 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation and Function of Fibroblast Growth Factor 8 and Its Function during Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neuron Development.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Sep 5;7:114. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00114. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27656162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast growth factor 8: Multifaceted role in development and developmental disorder.Genes Dis. 2025 Jan 10;12(5):101524. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101524. eCollection 2025 Sep. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40575596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The initiation and maintenance of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron identity in congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 27;14:1166132. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1166132. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37181038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological pathways leading to septo-optic dysplasia: a review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Apr 3;20(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03541-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40181463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of fibroblast growth factor 8 in cartilage development and disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Feb;26(4):990-999. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17174. Epub 2022 Jan 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35001536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic architecture of self-limited delayed puberty and congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 16;13:1069741. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1069741. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36726466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

