Non-coding RNAs in cancers with chromosomal rearrangements: the signatures, causes, functions and implications
- PMID: 31361891
- PMCID: PMC6884712
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz080
Non-coding RNAs in cancers with chromosomal rearrangements: the signatures, causes, functions and implications
Abstract
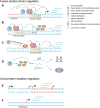
Chromosomal translocation leads to the juxtaposition of two otherwise separate DNA loci, which could result in gene fusion. These rearrangements at the DNA level are catastrophic events and often have causal roles in tumorigenesis. The oncogenic DNA messages are transferred to RNA molecules, which are in most cases translated into cancerous fusion proteins. Gene expression programs and signaling pathways are altered in these cytogenetically abnormal contexts. Notably, non-coding RNAs have attracted increasing attention and are believed to be tightly associated with chromosome-rearranged cancers. These RNAs not only function as modulators in downstream pathways but also directly affect chromosomal translocation or the associated products. This review summarizes recent research advances on the relationship between non-coding RNAs and chromosomal translocations and on diverse functions of non-coding RNAs in cancers with chromosomal rearrangements.
Keywords: chromosomal translocation; fusion protein; gene regulation; non-coding RNA; non-coding fusion transcript.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Competing Endogenous RNAs, Non-Coding RNAs and Diseases: An Intertwined Story.Cells. 2020 Jun 28;9(7):1574. doi: 10.3390/cells9071574. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32605220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow ectopic expression of a non-coding RNA in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a novel t(2;11)(q11.2;p15.1) translocation.Mol Cancer. 2008 Oct 23;7:80. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-80. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18947387 Free PMC article.
-
Current concepts of non-coding RNA regulation of immune checkpoints in cancer.Mol Aspects Med. 2019 Dec;70:117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Mol Aspects Med. 2019. PMID: 31582259 Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Regulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling and Cancer Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 4;16(12):28943-78. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226138. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26690121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic Role of Fusion-circRNAs Derived from Cancer-Associated Chromosomal Translocations.Cell. 2016 Apr 7;165(2):289-302. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.020. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27040497
Cited by
-
Breaking paradigms: Long non-coding RNAs forming gene fusions with potential implications in cancer.Genes Dis. 2023 Oct 11;11(3):101136. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101136. eCollection 2024 May. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38292185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Noncoding RNAs and the Epigenetics Machinery in Pediatric Tumors and Their Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 19;15(10):2833. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102833. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer fusion transcripts with human non-coding RNAs.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 11;14:1415801. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1415801. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38919532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease-Causing Mutations and Rearrangements in Long Non-coding RNA Gene Loci.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 30;11:527484. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.527484. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33329688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PFusionDB: a comprehensive database of plant-specific fusion transcripts.3 Biotech. 2024 Nov;14(11):282. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04132-1. Epub 2024 Oct 28. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39479298
References
-
- Antonescu C.R., Agaram N.P., Sung Y.S., et al. (2018). A distinct malignant epithelioid neoplasm with GLI1 gene rearrangements, frequent S100 protein expression, and metastatic potential: expanding the spectrum of pathologic entities with ACTB/MALAT1/PTCH1–GLI1 fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 42, 553–560. - PMC - PubMed

