Novel Treatment Targets Based on Insights in the Etiology of Depression: Role of IL-6 Trans-Signaling and Stress-Induced Elevation of Glutamate and ATP
- PMID: 31362361
- PMCID: PMC6789839
- DOI: 10.3390/ph12030113
Novel Treatment Targets Based on Insights in the Etiology of Depression: Role of IL-6 Trans-Signaling and Stress-Induced Elevation of Glutamate and ATP
Abstract
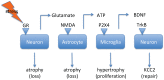
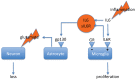
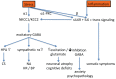
Inflammation and psychological stress are risk factors for major depression and suicide. Both increase central glutamate levels and activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system. Both factors also affect the function of the chloride transporters, Na-K-Cl-cotransporter-1 (NKCC1) and K-Cl-cotransporter-2 (KCC2), and provoke interleukin-6 (IL-6) trans-signaling. This leads to measurable increases in circulating corticosteroids, catecholamines, anxiety, somatic and psychological symptoms, and a decline in cognitive functions. Recognition of the sequence of pathological events allows the prediction of novel targets for therapeutic intervention. Amongst others, these include blockade of the big-K potassium channel, blockade of the P2X4 channel, TYK2-kinase inhibition, noradrenaline α2B-receptor antagonism, nicotinic α7-receptor stimulation, and the Sgp130Fc antibody. A better understanding of downstream processes evoked by inflammation and stress also allows suggestions for tentatively better biomarkers (e.g., SERPINA3N, MARCKS, or 13C-tryptophan metabolism).
Keywords: inflammasome; ketamine; major depressive disorder; suicide; vagus nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lim S.S., Vos T., Flaxman A.D., Danaei G., Shibuya K., Adair-Rohani H., Amann M., Anderson H.R., Andrews K.G., Aryee M., et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wittchen H.U., Jacobi F., Rehm J., Gustavsson A., Svensson M., Jonsson B., Olesen J., Allgulander C., Alonso J., Faravelli C., et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011;21:655–679. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.07.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beumer W., Gibney S.M., Drexhage R.C., Pont-Lezica L., Doorduin J., Klein H.C., Steiner J., Connor T.J., Harkin A., Versnel M.A., et al. The immune theory of psychiatric diseases: A key role for activated microglia and circulating monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012;92:959–975. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212100. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

