Estrogen Deficiency Potentiates Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 31362375
- PMCID: PMC6696236
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20153709
Estrogen Deficiency Potentiates Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
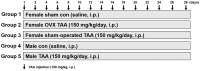
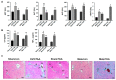
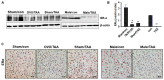
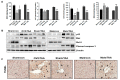
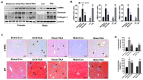
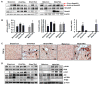
Hepatic fibrosis is characterized by persistent deposition of extracellular matrix proteins and occurs in chronic liver diseases. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether estrogen deficiency (ED) potentiates hepatic fibrosis in a thioacetamide (TAA)-treated rat model. Fibrosis was induced via intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) of TAA (150 mg/kg/day) for four weeks in ovariectomized (OVX) female, sham-operated female, or male rats. In TAA-treated OVX rats, the activities of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) were significantly increased compared to those in TAA-treated sham-operated OVX rats or TAA-treated male rats. Furthermore, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression was significantly increased compared to that in TAA-treated sham-operated rats. This was accompanied by the appearance of fibrosis biomarkers including vimentin, collagen-I, and hydroxyproline, in the liver of TAA-treated OVX rats. In addition, ED markedly reduced total glutathione (GSH) levels, as well as catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in TAA-treated OVX rats. In contrast, hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were elevated in TAA-treated OVX rats. Apoptosis significantly increased in TAA-treated OVX rats, as reflected by elevated p53, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase 3 levels. Significant increases in interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) concentrations were exhibited in TAA-treated OVX rats, and this further aggravated fibrosis through the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/Smad pathway. Our data suggest that ED potentiates TAA-induced oxidative damage in the liver, suggesting that ED may enhance the severity of hepatic fibrosis in menopausal women.
Keywords: collagen I; estrogen deficiency; liver fibrosis; thioacetamide; α-SMA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

