Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology
- PMID: 31362394
- PMCID: PMC6696197
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152749
Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology
Abstract
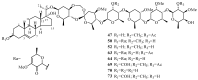
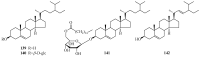
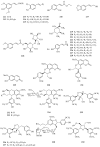
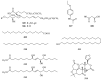
The genus Periploca belongs to the family Apocynaceae, which is composed of approximately ten species of plants according to incomplete statistics. Most of these plants serve as folk medicines with a long history, especially Periploca sepium and Periploca forrestii. The botanical classifications, chemical constituents, biological activities and toxicities of the genus Periploca were summarized in the literature from 1897 to early 2019. Though the botanical classification of this genus is controversial, these species are well-known to be rich sources of diverse and complex natural products-above all, cardiac steroids and C21 pregnane steroids with special structures and obvious pharmacological activities. The various crude extracts and 314 isolated metabolites from this genus have attracted much attention in intensive biological studies, indicating that they are equipped with cardiotonic, anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antitumor, antimicrobial, antioxidant, insecticidal and other properties. It is noteworthy that some cardiac glycosides showed hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity at certain doses. Therefore, in view of the medical and agricultural value of the genus Periploca, in-depth investigations of the pharmacology in vivo, the mechanisms of biological actions, and the pharmacokinetics of the active ingredients should be carried out in the future. Moreover, in order to ensure the safety of clinical medication, the potential toxicities of cardiac glycosides or other compounds should also be paid attention. This systematic review provides an important reference base for applied research on pharmaceuticals and pesticides from this genus.
Keywords: biological activities; classification; genus Periploca; phytochemistry; review; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
















References
-
- Stevens P.F. Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. [(accessed on 15 July 2019)];2017 Available online: http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/
-
- Flora of China Editorial Committee . Flora of China. Volume 16. Science Press; Beijing, China: Missouri Botanical Garden Press; St. Louis, MO, USA: 1995. pp. 189–196.
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Volume 1. Beijing Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2015. pp. 257–258.
-
- Editorial Board of Chinese Materia Medica, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine . Miao Medicine Volume of Chinese Materia Medica. Volume Miao Medicine. Guizhou science and technology press; Guiyang, China: 2005. pp. 526–527.
-
- Zhang Y.H., Wang F.P. Recent adcances of chemical constituents of Periploca plants. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2003;15:157–161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

