The Genetic Basis of Toxin Biosynthesis in Dinoflagellates
- PMID: 31362398
- PMCID: PMC6722697
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms7080222
The Genetic Basis of Toxin Biosynthesis in Dinoflagellates
Abstract
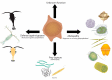
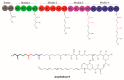
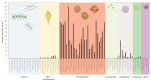
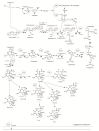
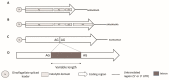
In marine ecosystems, dinoflagellates can become highly abundant and even dominant at times, despite their comparatively slow growth rates. One factor that may play a role in their ecological success is the production of complex secondary metabolite compounds that can have anti-predator, allelopathic, or other toxic effects on marine organisms, and also cause seafood poisoning in humans. Our knowledge about the genes involved in toxin biosynthesis in dinoflagellates is currently limited due to the complex genomic features of these organisms. Most recently, the sequencing of dinoflagellate transcriptomes has provided us with valuable insights into the biosynthesis of polyketide and alkaloid-based toxin molecules in dinoflagellate species. This review synthesizes the recent progress that has been made in understanding the evolution, biosynthetic pathways, and gene regulation in dinoflagellates with the aid of transcriptomic and other molecular genetic tools, and provides a pathway for future studies of dinoflagellates in this exciting omics era.
Keywords: alkaloids; dinoflagellates; polyketides; toxins; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors acknowledge that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis and molecular genetics of polyketides in marine dinoflagellates.Mar Drugs. 2010 Mar 31;8(4):1011-48. doi: 10.3390/md8041011. Mar Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20479965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates: A molecular overview.J Proteomics. 2016 Mar 1;135:132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 25. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26316331 Review.
-
Transcriptomic investigation into polyketide toxin synthesis in Ostreopsis (Dinophyceae) species.Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov;21(11):4196-4211. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14780. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31415128
-
Biosynthesis of Saxitoxin in Marine Dinoflagellates: An Omics Perspective.Mar Drugs. 2020 Feb 5;18(2):103. doi: 10.3390/md18020103. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32033403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of polyketide synthesis in dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum lima.Harmful Algae. 2023 Mar;123:102391. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2023.102391. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Harmful Algae. 2023. PMID: 36894212
Cited by
-
Identification of a Novel Saxitoxin Analogue, 12β-Deoxygonyautoxin 3, in the Cyanobacterium, Anabaena circinalis (TA04).Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 16;11(9):539. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090539. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31527551 Free PMC article.
-
The Common Sunstar Crossaster papposus-A Neurotoxic Starfish.Mar Drugs. 2021 Dec 7;19(12):695. doi: 10.3390/md19120695. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940694 Free PMC article.
-
Finding Species-Specific Extracellular Surface-Facing Proteomes in Toxic Dinoflagellates.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;13(9):624. doi: 10.3390/toxins13090624. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564629 Free PMC article.
-
Ostreopsis Schmidt and Coolia Meunier (Dinophyceae, Gonyaulacales) from Cook Islands and Niue (South Pacific Ocean), including description of Ostreopsis tairoto sp. nov.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 22;13(1):3110. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29969-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36813881 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of sxtA and rDNA qPCR assays through monitoring of an inshore bloom of Alexandrium catenella Group 1.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 10;9(1):14532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51074-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31601884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor F., Hoppenrath M., Saldarriaga J.F. Dinoflagellate diversity and distribution. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008;17:407–418. doi: 10.1007/s10531-007-9258-3. - DOI
-
- Keeling P.J., Burki F., Wilcox H.M., Allam B., Allen E.E., Amaral-Zettler L.A., Armbrust E.V., Archibald J.M., Bharti A.K., Bell C.J. The Marine Microbial Eukaryote Transcriptome Sequencing Project (MMETSP): illuminating the functional diversity of eukaryotic life in the oceans through transcriptome sequencing. PLoS Boil. 2014;12:e1001889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

