Tadalafil 5 mg Alone or in Combination with Tamsulosin 0.4 mg for the Management of Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction: Results of a Prospective Observational Trial
- PMID: 31362410
- PMCID: PMC6723816
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8081126
Tadalafil 5 mg Alone or in Combination with Tamsulosin 0.4 mg for the Management of Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction: Results of a Prospective Observational Trial
Abstract
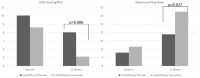
Tadalafil 5 mg represents the standard for men with Erectile dysfunction (ED) and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)/benign prostatic enlargement (BPE). We carried out an observational trial aiming to assess the efficacy and safety of Tadalafil compared with Tadalafil plus Tamsulosin. Seventy-five patients complaining of ED and LUTS were treated for 12-weeks with Tadalafil plus placebo (TAD+PLA-group) or with combination therapy tadalafil plus tamsulosin (TAD+TAM-group). Efficacy variables were: International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) and safety assessments. Data were evaluated using paired samples T-test (baseline vs. 12-weeks) and analysis of variance (Δgroup-TAD+PLA vs. Δgroup-TAD+TAM). At baseline, both groups presented similar characteristics and symptoms scores (all: p > 0.05). From baseline to 12-weeks, all the subjects showed a significant improvement of IIEF, total-IPSS, storage-IPSS, Qmax (all: p < 0.001). Conversely, a significant improvement of voiding-IPSS was observed in TAD+TAM-group (-3.5 points, p < 0.001). Indeed, TAD+PLA-group showed a not significant improvement of voiding-IPSS (-2.0 points, p = 0.074). When we compared between-groups differences at 12-weeks, IIEF (p = 0.255), total-IPSS (p = 0.084) and storage-IPSS (p = 0.08) did not show any statistically significant differences, whereas, voiding-IPSS and Qmax were significantly better in TAD+TAM-group (p = 0.006 and p = 0.027, respectively). No severe treatment adverse events (TAEs) were reported in both groups. Tadalafil achieved the same improvements of IIEF, total-IPSS, storage-IPSS when compared to combination therapy. Instead, Qmax and voiding-IPSS were better managed with combination therapy, without change of TAEs.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; erectile dysfunction; lower urinary tract symptoms; medical therapy; tadalafil; tamsulosin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Which Drug to Discontinue 3 Months After Combination Therapy of Tadalafil plus Tamsulosin for Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptom and Erectile Dysfunction? Results of a Prospective Observational Trial.Eur Urol Focus. 2021 Mar;7(2):432-439. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2019.09.015. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Eur Urol Focus. 2021. PMID: 31606473
-
A comparative randomized prospective study to evaluate efficacy and safety of combination of tamsulosin and tadalafil vs. tamsulosin or tadalafil alone in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia.J Sex Med. 2014 Jan;11(1):187-96. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12357. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Sex Med. 2014. PMID: 24165272 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of a Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy of Tamsulosin and Tadalafil for Patients With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blinded, Active-Controlled Trial.J Sex Med. 2017 Aug;14(8):1018-1027. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.06.006. J Sex Med. 2017. PMID: 28760246 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil Plus Tamsulosin Compared with Tadalafil Alone in Treating Men with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Erectile Dysfunction.Am J Mens Health. 2019 Sep-Oct;13(5):1557988319882597. doi: 10.1177/1557988319882597. Am J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 31625449 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Tadalafil versus Tamsulosin in Treating Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Suggestive of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Apr 24;26:e923179. doi: 10.12659/MSM.923179. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32327621 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study of tamsulosin versus tadalafil in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. A prospective randomized study.Urol Ann. 2022 Jul-Sep;14(3):236-240. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_6_21. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Urol Ann. 2022. PMID: 36117785 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Combination Comprising Tamsulosin and PDE5-Is, Relative to Monotherapies, in Treating Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction Associated With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Meta-Analysis.Am J Mens Health. 2021 Jan-Feb;15(1):1557988321997725. doi: 10.1177/1557988321997725. Am J Mens Health. 2021. PMID: 33632007 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Review of Combined Phosphodiesterase-5-Inhibitors and α-Blockers versus Phosphodiesterase-5-Inhibitors Alone for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Arab J Urol. 2023 Jun 13;22(1):13-23. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2023.2220627. eCollection 2024. Arab J Urol. 2023. PMID: 38205391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discontinuation Rates of Tadalafil Alone and in Combination with a-Blockers in the Treatment of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms with or without Coexisting Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Clin Pract. 2022 Nov 3;2022:9298483. doi: 10.1155/2022/9298483. eCollection 2022. Int J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36419863 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil Alone or in Combination with Tamsulosin for the Management for LUTS/BPH and ED.Curr Urol Rep. 2020 Oct 27;21(12):56. doi: 10.1007/s11934-020-01009-7. Curr Urol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33108544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gacci M., Eardley I., Giuliano F., Hatzichristou D., Kaplan S.A., Maggi M., McVary K.T., Mirone V., Porst H., Roehrborn C.G. Critical analysis of the relationship between sexual dysfunctions and lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur. Urol. 2011;60:809–825. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.06.037. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbosa J.A., Muracca E., Nakano É., Assalin A.R., Cordeiro P., Paranhos M., Cury J., Srougi M., Antunes A.A. Interactions between lower urinary tract symptoms and cardiovascular risk factors determine distinct patterns of erectile dysfunction: A latent class analysis. J. Urol. 2013;190:2177–2182. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.05.048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gravas S., Bach T., Drake M., Gacci M., Gratzke C., Herrmann T.R.W., Madersbacher S., Mamoulakis C., Tikkinen K.A.O. Treatment of Non-Neurogenic Male LUTS. [(accessed on 7 May 2019)];2017 Available online: http://uroweb.org/guideline/treatment-of-non-neurogenic-male-luts/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

