Tangeretin-Assisted Platinum Nanoparticles Enhance the Apoptotic Properties of Doxorubicin: Combination Therapy for Osteosarcoma Treatment
- PMID: 31362420
- PMCID: PMC6723885
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9081089
Tangeretin-Assisted Platinum Nanoparticles Enhance the Apoptotic Properties of Doxorubicin: Combination Therapy for Osteosarcoma Treatment
Abstract
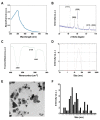
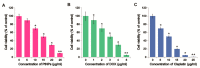
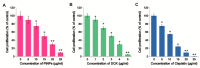
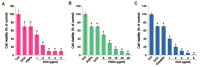
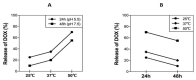
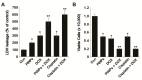
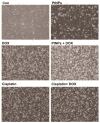
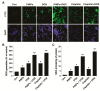
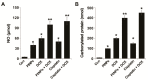
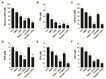
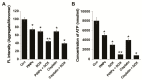
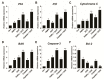
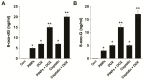
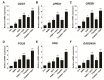
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common type of cancer and the most frequent malignant bone tumor in childhood and adolescence. Nanomedicine has become an indispensable field in biomedical and clinical research, with nanoparticles (NPs) promising to increase the therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs. Doxorubicin (DOX) is a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug against OS; however, it causes severe side effects that restrict its clinical applications. Here, we investigated whether combining platinum NPs (PtNPs) and DOX could increase their anticancer activity in human bone OS epithelial cells (U2OS). PtNPs with nontoxic, effective, thermally stable, and thermoplasmonic properties were synthesized and characterized using tangeretin. We examined the combined effects of PtNPs and DOX on cell viability, proliferation, and morphology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide, protein carbonyl content, antioxidants, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), adenosine tri phosphate (ATP) level, apoptotic and antiapoptotic gene expression, oxidative stress-induced DNA damage, and DNA repair genes. PtNPs and DOX significantly inhibited U2OS viability and proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, increasing lactate dehydrogenase leakage, ROS generation, and malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, and carbonylated protein levels. Mitochondrial dysfunction was confirmed by reduced MMP, decreased ATP levels, and upregulated apoptotic/downregulated antiapoptotic gene expression. Oxidative stress was a major cause of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity, confirmed by decreased levels of various antioxidants. Furthermore, PtNPs and DOX increased 8-oxo-dG and 8-oxo-G levels and induced DNA damage and repair gene expression. Combination of cisplatin and DOX potentially induce apoptosis comparable to PtNPs and DOX. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to describe the combined effects of PtNPs and DOX in OS.
Keywords: DNA damage; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; doxorubicin; genotoxicity; oxidative stress; platinum nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platinum Nanoparticles in Biomedicine: Preparation, Anti-Cancer Activity, and Drug Delivery Vehicles.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 23;13:797804. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.797804. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35281900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Properties of Platinum Nanoparticles and Retinoic Acid: Combination Therapy for the Treatment of Human Neuroblastoma Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 16;21(18):6792. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186792. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32947930 Free PMC article.
-
Anisotropic Platinum Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis, Inflammatory Response, and Transcriptomic and Molecular Pathways in Human Acute Monocytic Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 9;21(2):440. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020440. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936679 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Apigenin-Biosynthesized Ultra-Small Platinum Nanoparticles on the Human Monocytic THP-1 Cell Line.Cells. 2019 May 10;8(5):444. doi: 10.3390/cells8050444. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31083475 Free PMC article.
-
Platinum nanoparticles in cancer therapy: chemotherapeutic enhancement and ROS generation.Med Oncol. 2025 Jan 9;42(2):42. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02598-w. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39789336 Review.
Cited by
-
Palladium Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Apoptosis, and Immunomodulation Enhance the Biogenesis and Release of Exosome in Human Leukemia Monocytic Cells (THP-1).Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Apr 15;16:2849-2877. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S305269. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33883895 Free PMC article.
-
Platinum Nanoparticles in Biomedicine: Preparation, Anti-Cancer Activity, and Drug Delivery Vehicles.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 23;13:797804. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.797804. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35281900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platinum Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Biomedical Applications.Molecules. 2020 Oct 28;25(21):4981. doi: 10.3390/molecules25214981. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33126464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using biometabolites: mechanisms and applications.Biometals. 2025 Feb;38(1):21-54. doi: 10.1007/s10534-024-00642-w. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Biometals. 2025. PMID: 39377881 Review.
-
Role of green synthesized platinum nanoparticles in cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis of human colon cancer cells (HCT-116).Heliyon. 2022 Nov 26;8(12):e11917. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11917. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36506358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz C.L., Gorlick R., Teot L., Krailo M., Chen Z., Goorin A., Grier H.E., Bernstein M.L., Meyers P. Multiple drug resistance in osteogenic sarcoma: INT0133 from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:2057–2062. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.7776. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

