Therapeutic Perspectives of Molecules from Urtica dioica Extracts for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 31362429
- PMCID: PMC6695697
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152753
Therapeutic Perspectives of Molecules from Urtica dioica Extracts for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
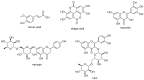
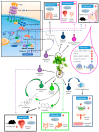
A large range of chronic and degenerative diseases can be prevented through the use of food products and food bioactives. This study reports the health benefits and biological activities of the Urtica dioica (U. dioica) edible plant, with particular focus on its cancer chemopreventive potential. Numerous studies have attempted to investigate the most efficient anti-cancer therapy with few side effects and high toxicity on cancer cells to overcome the chemoresistance of cancer cells and the adverse effects of current therapies. In this regard, natural products from edible plants have been assessed as sources of anti-cancer agents. In this article, we review current knowledge from studies that have examined the cytotoxic, anti-tumor and anti-metastatic effects of U. dioica plant on several human cancers. Special attention has been dedicated to the treatment of breast cancer, the most prevalent cancer among women and one of the main causes of death worldwide. The anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of U. dioica have been demonstrated on different human cancers, investigating the properties of U. dioica at cellular and molecular levels. The potent cytotoxicity and anti-cancer activity of the U. dioica extracts are due to its bioactive natural products content, including polyphenols which reportedly possess anti-oxidant, anti-mutagenic and anti-proliferative properties. The efficacy of this edible plant to prevent or mitigate human cancers has been demonstrated in laboratory conditions as well as in experimental animal models, paving the way to the development of nutraceuticals for new anti-cancer therapies.
Keywords: Urtica dioica; breast cancer; cancer therapy; food bioactives; natural products bioactivity; nutraceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytochemical, Anti-diabetic and Cardiovascular Properties of Urtica dioica L. (Urticaceae): A Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019;19(1):63-71. doi: 10.2174/1389557518666180924121528. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30246639 Review.
-
Urtica dioica inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis by targeting Ornithine decarboxylase and Adenosine deaminase as key regulatory enzymes in adenosine and polyamines homeostasis in human breast cancer cell lines.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018 Feb 28;64(3):97-102. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2018.64.3.16. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018. PMID: 29506637
-
Urtica dioica dichloromethane extract induce apoptosis from intrinsic pathway on human prostate cancer cells (PC3).Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Mar 31;62(3):78-83. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27064877
-
Screening of pharmacological uses of Urtica dioica and others benefits.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;150:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31163183 Review.
-
Antioxidant and apoptotic effects of an aqueous extract of Urtica dioica on the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5317-23. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.9.5317. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24175819
Cited by
-
Anticancer Effects of Urtica Dioica in Breast Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Feb 1;23(2):673-681. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.2.673. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 35225481 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Composition of Urtica dioica Essential Oil with Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(5):728-739. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220829104541. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 36043715
-
Urtica dioica Mediates Zinc-Copper Doped Nanoparticles as Potent Anticancer Agents against Human Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cell Line.Adv Biomed Res. 2025 Apr 30;14:30. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_515_23. eCollection 2025. Adv Biomed Res. 2025. PMID: 40390818 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Nettle Tea on SKOV-3 Ovarian Cancer Cells Through ROS Production, Apoptosis Induction, and Motility Inhibition Without Altering Autophagy.Foods. 2024 Oct 21;13(20):3336. doi: 10.3390/foods13203336. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39456397 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant GNLY is linked to Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.Hum Genet. 2019 Dec;138(11-12):1267-1274. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02066-w. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31642954
References
-
- Wildman R.E.C., Wildman R., Wallace T.C. Handbook of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2016.
-
- Angela M., Meireles A. Extracting Bioactive Compounds for Food Products: Theory and Applications. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2008.
-
- Kavalali G.M. Urtica Therapeutic and Nutritional Aspects of Stinging Nettles. Volume 37 Taylor & Francis; London, UK: 2003.
-
- Upton R. Stinging nettles leaf (Urtica dioica L.): Extraordinary vegetable medicine. J. Herb. Med. 2013;3:9–38. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2012.11.001. - DOI
-
- Ahmed K.K.M., Parsuraman S. Urtica dioica L., (Urticaceae): A Stinging Nettle. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2014;5:6–8. doi: 10.5530/srp.2014.1.3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

