Laboratory Investigation of Lignocellulosic Biomass as Performance Improver for Bituminous Materials
- PMID: 31362441
- PMCID: PMC6722804
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11081253
Laboratory Investigation of Lignocellulosic Biomass as Performance Improver for Bituminous Materials
Abstract
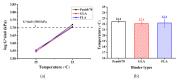
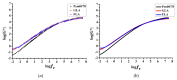
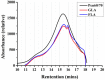
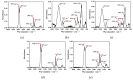
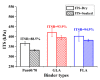
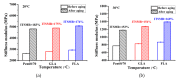
Lignocellulosic biomass has gained increasing attention as a performance modifier for bituminous material due to the vast amount available, its low cost and its potential to improve the durability of pavement. However, a comprehensive study concerning both the binder and mixture performance of modified bituminous material with lignocellulose is still limited. This research aims to evaluate the feasibility of applying lignocellulose as bitumen modifier by rheological, chemical and mechanical tests. To this end, two lignocellulosic biomass modified bituminous binders and corresponding mixtures were prepared and tested. The chemical characterization revealed the interaction between lignocellulosic biomass and bitumen fractions. Rheological test results have shown that lignocellulosic modifiers improve the overall performance of bituminous binder at high, intermediate and low temperatures. The findings obtained by mixture mechanical tests were identical to the binder test results, proving the positive effect of lignocellulosic biomass on overall paving performance of bituminous materials. Although lignocellulosic modifier slightly deteriorates the bitumen workability, the modified bitumen still meets the viscosity requirements mentioned in Superpave specification. This paper suggests that lignocellulosic biomass is a promising modifier for bituminous materials with both engineering and economic merits. Future study will focus on field validation and life cycle assessment of bituminous pavement with lignocellulosic biomass.
Keywords: bitumen modifier; lignocellulosic biomass; mechanical properties; rheological tests; workability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Ciolacu D., Ciolacu F., Popa V.I. Amorphous cellulose-structure and characterization. Cell Chem. Technol. 2011;45:13–21.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

