Purification and Characterization of Ornithine Decarboxylase from Aspergillus terreus; Kinetics of Inhibition by Various Inhibitors
- PMID: 31362455
- PMCID: PMC6696095
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152756
Purification and Characterization of Ornithine Decarboxylase from Aspergillus terreus; Kinetics of Inhibition by Various Inhibitors
Abstract
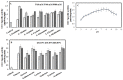
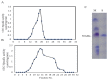
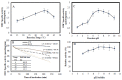
l-Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is the rate-limiting enzyme of de novo polyamine synthesis in humans and fungi. Elevated levels of polyamine by over-induction of ODC activity in response to tumor-promoting factors has been frequently reported. Since ODC from fungi and human have the same molecular properties and regulatory mechanisms, thus, fungal ODC has been used as model enzyme in the preliminary studies. Thus, the aim of this work was to purify ODC from fungi, and assess its kinetics of inhibition towards various compounds. Forty fungal isolates were screened for ODC production, twenty fungal isolates have the higher potency to grow on L-ornithine as sole nitrogen source. Aspergillus terreus was the most potent ODC producer (2.1 µmol/mg/min), followed by Penicillium crustosum and Fusarium fujikuori. These isolates were molecularly identified based on their ITS sequences, which have been deposited in the NCBI database under accession numbers MH156195, MH155304 and MH152411, respectively. ODC was purified and characterized from A. terreus using SDS-PAGE, showing a whole molecule mass of ~110 kDa and a 50 kDa subunit structure revealing its homodimeric identity. The enzyme had a maximum activity at 37 °C, pH 7.4-7.8 and thermal stability for 20 h at 37 °C, and 90 days storage stability at 4 °C. A. terreus ODC had a maximum affinity (Km) for l-ornithine, l-lysine and l-arginine (0.95, 1.34 and 1.4 mM) and catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) (4.6, 2.83, 2.46 × 10-5 mM-1·s-1). The enzyme activity was strongly inhibited by DFMO (0.02 µg/mL), curcumin (IC50 0.04 µg/mL), propargylglycine (20.9 µg/mL) and hydroxylamine (32.9 µg/mL). These results emphasize the strong inhibitory effect of curcumin on ODC activity and subsequent polyamine synthesis. Further molecular dynamic studies to elucidate the mechanistics of ODC inhibition by curcumin are ongoing.
Keywords: Aspergillus terreus; curcumin; inhibition; kinetics; ornithine decarboxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gupta K., Dey A., Gupta B. Plant polyamines in abiotic stress responses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013;35:2015–2036. doi: 10.1007/s11738-013-1239-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

