Novel Benzothiazole-based Ureas as 17β-HSD10 Inhibitors, A Potential Alzheimer's Disease Treatment
- PMID: 31362457
- PMCID: PMC6696238
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152757
Novel Benzothiazole-based Ureas as 17β-HSD10 Inhibitors, A Potential Alzheimer's Disease Treatment
Abstract
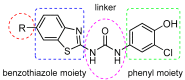
: It has long been established that mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients can trigger pathological changes in cell metabolism by altering metabolic enzymes such as the mitochondrial 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 (17β-HSD10), also known as amyloid-binding alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD). We and others have shown that frentizole and riluzole derivatives can inhibit 17β-HSD10 and that this inhibition is beneficial and holds therapeutic merit for the treatment of AD. Here we evaluate several novel series based on benzothiazolylurea scaffold evaluating key structural and activity relationships required for the inhibition of 17β-HSD10. Results show that the most promising of these compounds have markedly increased potency on our previously published inhibitors, with the most promising exhibiting advantageous features like low cytotoxicity and target engagement in living cells.
Keywords: 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 (17β-HSD10), amyloid binding alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD), benzothiazole; Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ), mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
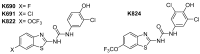
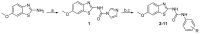
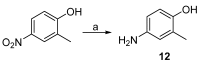
Similar articles
-
Benzothiazolyl Ureas are Low Micromolar and Uncompetitive Inhibitors of 17β-HSD10 with Implications to Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 17;21(6):2059. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062059. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32192199 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of benzothiazole-based ureas as potential ABAD/17β-HSD10 modulators for Alzheimer's disease treatment.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Aug 1;26(15):3675-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.05.087. Epub 2016 May 30. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27287370
-
Synthesis and evaluation of frentizole-based indolyl thiourea analogues as MAO/ABAD inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease treatment.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Feb 1;25(3):1143-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.12.029. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28082069
-
Involvement of Type 10 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase in the Pathogenesis of Infantile Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17604. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417604. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infantile Neurodegeneration Results from Mutants of 17β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 10 Rather Than Aβ-Binding Alcohol Dehydrogenase.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 9;24(10):8487. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108487. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic value of thiazole and thiazolidine derivatives in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic literature review.Res Pharm Sci. 2024 Feb 6;19(1):1-12. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.394816. eCollection 2024 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39006977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico and In Vivo Evaluation of Novel 2-Aminobenzothiazole Derivative Compounds as Antidiabetic Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):909. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030909. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940678 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Biological Importance of 2-(thio)ureabenzothiazoles.Molecules. 2022 Sep 19;27(18):6104. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186104. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benzothiazolyl Ureas are Low Micromolar and Uncompetitive Inhibitors of 17β-HSD10 with Implications to Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 17;21(6):2059. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062059. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32192199 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 and amyloid-β 42 derived cytotoxicity relevant to Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jul 23;17(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01821-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40702546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benek O., Aitken L., Hroch L., Kuca K., Gunn-Moore F., Musilek K. A Direct interaction between mitochondrial proteins and amyloid-β peptide and its significance for the progression and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015;22:1056–1085. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150114163051. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/18_069/0010054/Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of Czech Republic
- Faculty of Science, no. VT2019-2021, SV2115-2018/University of Hradec Kralove
- 40th Anniversary Award/RS MacDonald Charitable Trust
- 291/Alzheimer's Society/United Kingdom
- ISSF3 University of St Andrews/WT-ISSF
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

