Role of RIN4 in Regulating PAMP-Triggered Immunity and Effector-Triggered Immunity: Current Status and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 31362467
- PMCID: PMC6681865
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2019.2433
Role of RIN4 in Regulating PAMP-Triggered Immunity and Effector-Triggered Immunity: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Abstract
As sessile organisms, plants have developed sophisticated system to defend themselves against microbial attack. Since plants do not have specialized immune cells, all plant cells appear to have the innate ability to recognize pathogens and turn on an appropriate defense response. The plant innate immune system has two major branches: PAMPs (pathogen associated molecular patterns)-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). The ability to discriminate between self and non-self is a fundamental feature of living organisms, and it is a prerequisite for the activation of plant defenses specific to microbial infection. Arabidopsis cells express receptors that detect extracellular molecules or structures of the microbes, which are called collectively PAMPs and activate PTI. However, nucleotidebinding site leucine-rich repeats (NB-LRR) proteins mediated ETI is induced by direct or indirect recognition of effector molecules encoded by avr genes. In Arabidopsis, plasmamembrane localized multifunctional protein RIN4 (RPM1interacting protein 4) plays important role in both PTI and ETI. Previous studies have suggested that RIN4 functions as a negative regulator of PTI. In addition, many different bacterial effector proteins modify RIN4 to destabilize plant immunity and several NB-LRR proteins, including RPM1 (resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola 1), RPS2 (resistance to P. syringae 2) guard RIN4. This review summarizes the current studies that have described signaling mechanism of RIN4 function, modification of RIN4 by bacterial effectors and different interacting partner of RIN4 in defense related pathway. In addition, the emerging role of the RIN4 in plant physiology and intercellular signaling as it presents in exosomes will be discussed.
Keywords: AvrB; AvrRpm1; AvrRpt2; PAMP-triggered immunity; RIN4; effector-triggered immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
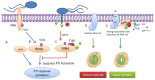
 , AvrB:
, AvrB:
 , AvrRpm1:
, AvrRpm1:
 , RIPK:
, RIPK:
 .
.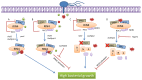
 , AvrB:
, AvrB:
 , AvrRpm1:
, AvrRpm1:
 , RIPK:
, RIPK:
 , ROC1:
, ROC1:
 , NDR1:
, NDR1:
 .
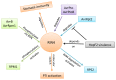
.
References
-
- Axelsen K.B., Venema K., Jahn T., Baunsgaard L., Palmgren M.G. Molecular dissection of the C-terminal regulatory domain of the plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase AHA2: mapping of residues that when altered give rise to an activated enzyme. Biochemistry. 1999;38:7227–7234. doi: 10.1021/bi982482l. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

